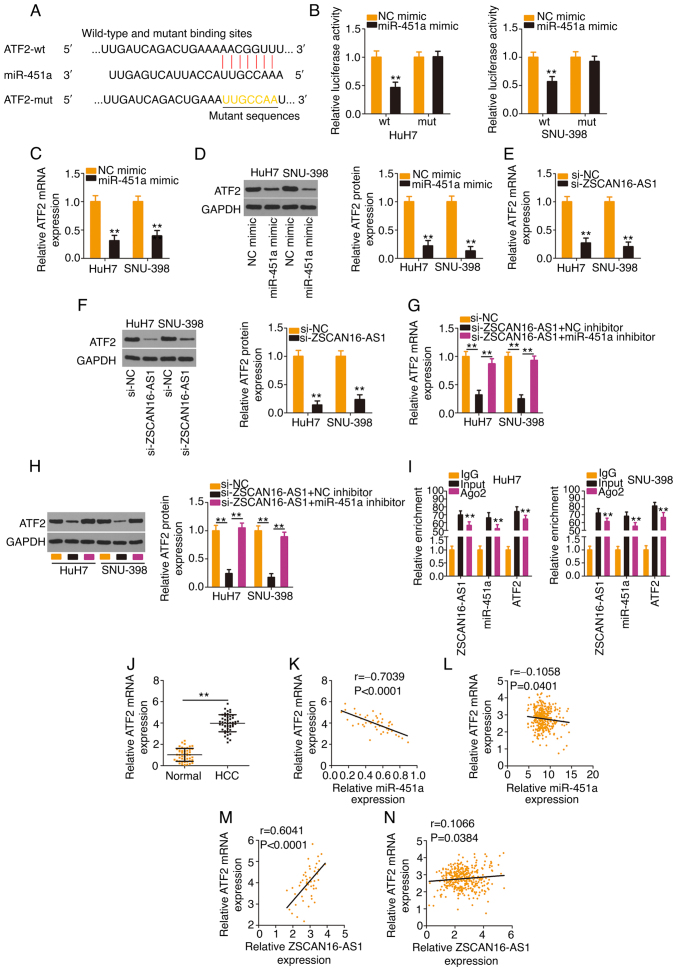
Figure 5.
The ZSCAN16-AS1/miR-451a axis regulates ATF2 expression in HCC cells. (A) The predicted binding site of miR-451a within the 3′-UTR of ATF2. The mutated binding site is also shown. (B) HCC cells were transfected with ATF2-wt or ATF2-mut in combination with miR-451a mimic or NC mimic; 48 h later, the luciferase activity was quantified. (C and D) ATF2 expression was determined in HCC cells when miR-451a was overexpressed. (E) mRNA and (F) protein expression of ATF2 in HCC cells following ZSCAN16-AS1 ablation. si-ZSCAN16-AS1 together with miR-451a inhibitor or NC inhibitor was transfected into HCC cells, followed by quantification of ATF2 (G) mRNA and (H) protein levels. (I) RNA immunoprecipitation was used to assess ZSCAN16-AS1, miR-451a and ATF2 enrichment in immunoprecipitants in HCC cells. (J) ATF2 level was determined in HCC tissues using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. (K) The correlation of ATF2 mRNA and miR-451a expression in 47 HCC tissues. (L) The expression correlation between ATF2 and miR-451a in HCC was examined using TCGA database. (M) The relation between ATF2 mRNA and ZSCAN16-AS1 in 47 HCC tissues. (N) The expression correlation between ZSCAN16-AS1 and ATF2 in HCC was examined using TCGA database. **P<0.01. miR, microRNA; ATF2, activating transcription factor 2; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; UTR, untranslated region; wt, wild-type; mut, mutant; NC, negative control; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; si, small interfering.