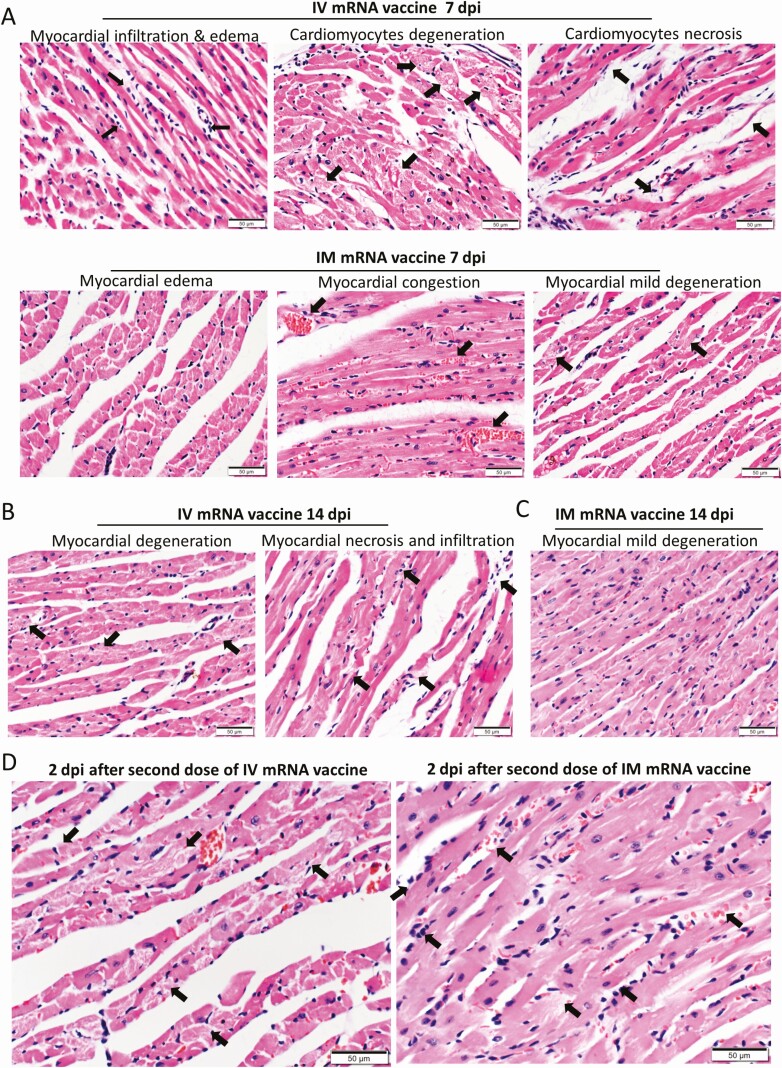
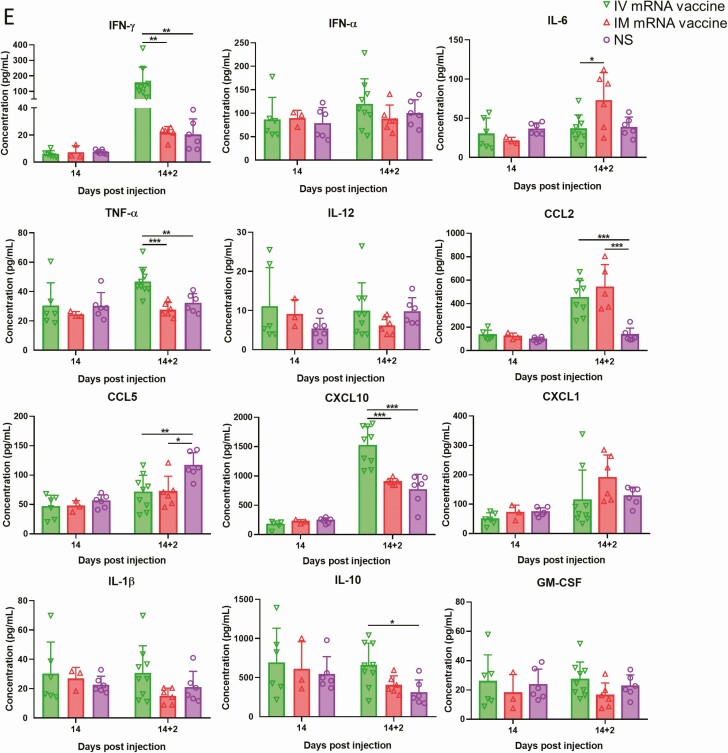
Figure 7.
Histopathological changes in the heart at 7 and 14 dpi after first dose of IV or IM mRNA vaccine and 2 dpi after second dose of vaccine. Groups of mice were given IV and IM vaccine or NS as control. At 7–14 dpi, mice were killed for histopathology. Another 2 groups of mice were given second dose of IV or IM mRNA vaccine at 14 days after the first priming dose and sacrificed at 2 dpi after the second boosting dose. A, Representative histopathological images of mouse heart at day 7. Top panel consisted of heart sections of IV group, which showed myocardial infiltration by white blood cells (left, arrows), interstitial edema, cardiomyocytes degeneration (middle, arrows) and necrosis (right, arrows). Lower panel consisted of heart sections from IM group, which showed myocardial interstitial edema (left) and myocardial vascular congestion (middle, arrows), with degeneration of a few cardiomyocytes (right, arrows). B, Representative histopathological images of IV and IM group at day 14. Heart in IV group showed persistent changes of cardiomyocyte degeneration, white blood cell infiltration, and foci of necrosis (arrows). C, Heart of mice in IM group showed minimal degeneration and infiltration but no necrosis. D, Representative histopathological images of the heart at 2 dpi after the second boosting dose given on day 14 after the first priming dose. Mouse heart in both IV and IM second dose group showed interstitial edema and diffuse cardiomyocyte degeneration on the left (arrows). Mouse heart in both IM and IV group showed diffuse inflammatory infiltrate, focal hemorrhage and necrosis (arrows, right). E. Serum cytokine/chemokine concentrations at 2 dpi post second dose were detected by beads-based multiplex flow cytometer assay. The NS group was used as control. Error bars indicated mean ± standard deviation. n = 5 each group. n = 9 for IV second dose boost group, n = 6 for IM second dose boost group and NS control group. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 by multiple t test. Abbreviations: dpi, days post-injection; IM, intramuscular; IV, intravenous; mRNA, messenger RNA; NS, normal saline; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction.