Figure 8.
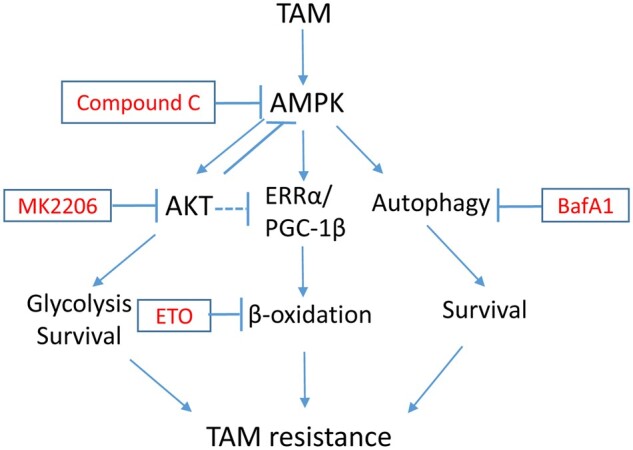
The proposed model. TAM treatment leads to activation of AMPK. Cells with chronic treatment of TAM also have elevated activation of AKT due to activation of receptor tyrosine kinases and PI3K. AMPK activation promotes AKT activation, while inhibition of AKT feedback-activates AMPK. AKT inhibition and AMPK activation promote ERRα and PGC-1β expression. AMPK additionally inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase. These lead to increased FAO. AMPK also promotes autophagy by direct phosphorylation of ULK1. Thus, inhibition of AKT can feedback-activate FAO and autophagy that promote cell survival and TAM resistance. Coinhibition of AKT and FAO or autophagy is necessary to overcome TAM resistance.
