Fig. 2.
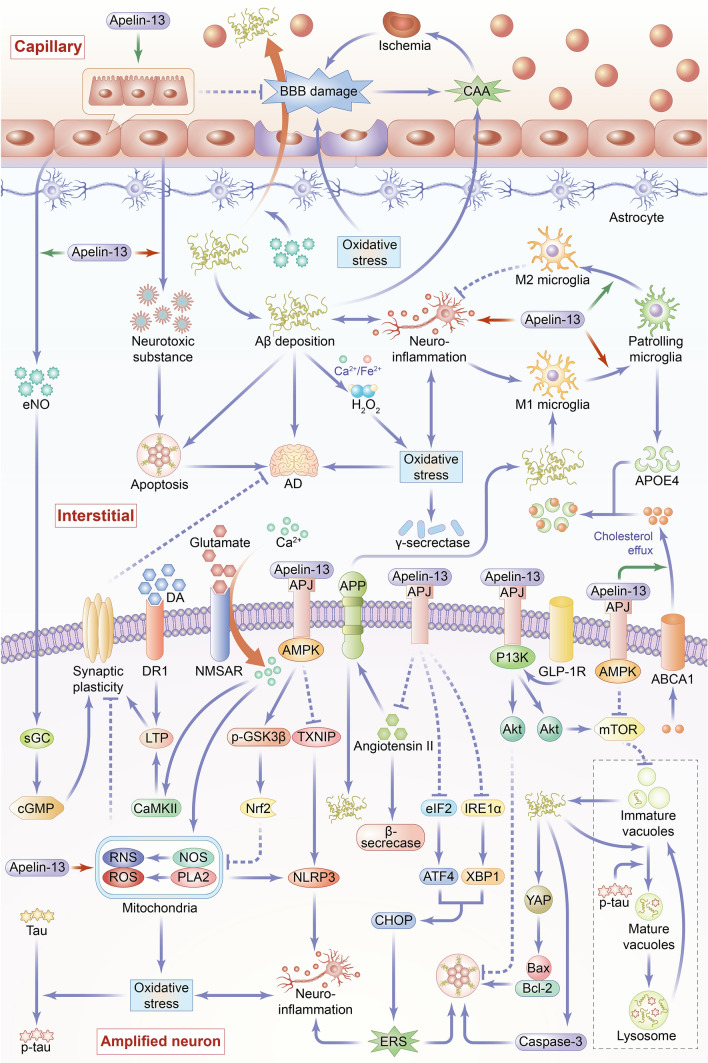
Overview of the main mechanisms and signaling pathways of Apelin-13 in regulating Alzheimer’s disease. The pathogenesis of AD is complex and diverse, and its occurrence and development are closely related to many factors, such as increased apoptosis, enhanced autophagy, synaptic plasticity disorder, elevated level of neuroinflammation, increased oxidative stress, destruction of blood brain barrier (BBB), formation of cerebrovascular amyloid angiopathy (CAA), and unesterified apolipoprotein E (APOE4). Apelin-13 plays an anti-AD role through the following mechanisms. 1. Apoptosis (1) Apelin-13 inhibits the production and aggregation of β-amyloid protein (Aβ), whereas Aβ induces apoptosis by regulating the Yes-related proteins-related protein (YAP) to increase the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and promote caspase-3 protein expression. (2) Apelin-13 inhibits the cell apoptosis by promoting Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) expression. (3) Apelin-13 enhances phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway to inhibit neuronal apoptosis. (4) Apelin-13 reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) by inhibiting inositol-requiring enzyme α (IRE-1α)/X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1)/C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2)/activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4)/CHOP signaling pathways, thereby inhibiting cell apoptosis. 2. Autophagy Apelin-13 paly a both promoting and inhibiting roles in autophagy through activation of (AMP-activated protein kinase) AMPK/(mammalian target of rapamycin) mTOR/(UNC-51-like kinase 1) ULK1 signaling pathway and of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Apelin-13 exerts its anti-AD effects mainly through the inhibition of cellular autophagy, which inhibits the formation of immature autophagy follicles and produce of Aβ. 3. Synaptic plasticity (1) Apelin-13 activates soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) and increases the level of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) through endothelial nitric oxide (eNO) signal pathway then improves synaptic plasticity. (2) Normally, N-methyl d-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) induce long term potentiation to improve synaptic plasticity. Apelin-13 inhibits oxidative stress induced by overactivated NMDAR, thereby reducing synaptic damage and improving synaptic plasticity. (3) Apelin-13 increases dopaminergic receptor 1 (DR1) levels and promotes DA-induced LTP, thereby promoting synaptic plasticity. 4. Neuroinflammation (1) Apelin-13 exerts an anti-inflammatory role by promoting microglia polarization to M2 phenotype and inhibiting microglia polarization to M1 phenotype. (2) Apelin-13 reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced oxidative damage in mitochondria and inflammatory response induced by nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome activation. (3) Apelin-13 reduces ERS, thus inhibiting neuroinflammation. 5. Oxidative stress (1) Apelin-13 inhibits NMDAR activity, sequentially inhibiting the production of ROS and reactive nitrogen species caused by excessive calcium ion influx. (2) Apelin-13 inhibits Aβ aggregation, which interacts with Fe2+ or Cu2+ to produce H2O2 which induces oxidative stress. (3) Apelin-13 induces the expression of antioxidant protein through AMPK/P-GSK-3β/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway or AMPK/thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP)/NLRP3 signal pathway, which relive oxidative stress-related cell damage. 6. BBB (1) Apelin-13 promotes vascular endothelial cell proliferation. (2) Apelin-13 inhibits oxidative stress-mediated BBB damage. 7. CAA (1) Apelin-13 promotes endothelial nitric oxide (eNO) secretion by vascular endothelium, and thus enhances the ability of vascular transmembrane transport to Aβ, thereby promoting the clearance of Aβ and inhibiting CAA. (2) Apelin-13 has an inhibitory effect on CAA by inhibiting the increase of β and γ secretase activity mediated by oxidative stress. (3) Apelin-13 inhibits the angiotensin II signaling pathway, thereby decreasing the activity of β-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1/β-secretase and inhibiting the generation of amyloid precursor protein (APP), playing an inhibitory effect on CAA. (4) Apelin-13 promotes the internalization of APOE4 that reduces the level of Aβ in intertissue-fluid, thus inhibiting CAA. 8. APOE4 Apelin-13 promotes the expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) protein, which facilitates cholesterol outflow to promote the lipidation of APOE, and thus enhances APOE4 internalization