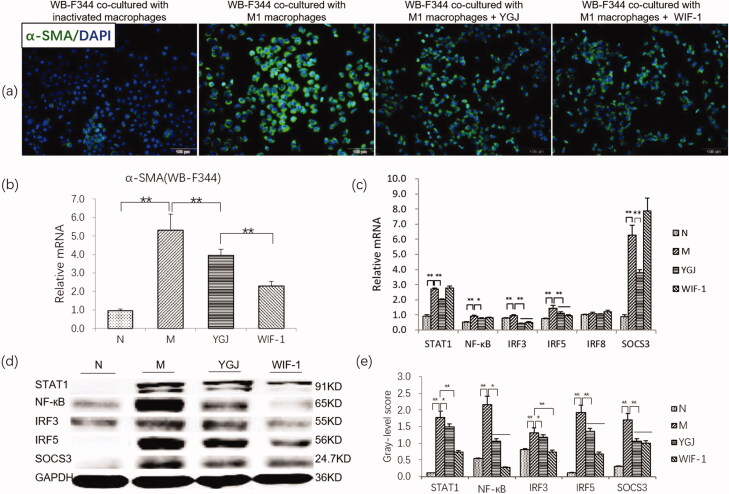
Figure 4.
YGJ inhibits the differentiation of WB-F344 cells into myofibroblasts through inhibiting the activation of M1 macrophages. (a) α-SMA immunofluorescent staining (green) in WB-F344 cells (×200) (the presented in vitro experiments were conducted in the same batch, the normal and model groups used the same pictures as published articles. The figures of WB-F344 co-cultured with inactivated macrophages and WB-F344 co-cultured with M1 macrophages were reused form a previous study [Ying Xu et al. 2018] and are reproduced with permission here). (b) α-SMA mRNA expression in WB-F344 cells was measured by RT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH mRNA (n = 3 per group). (c) STAT1, NF-κB, IRF3, IRF5, IRF8, and SOCS3 mRNA expressions in RAW264.7 cells were measured by RT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH mRNA (n = 3 per group); (d) STAT1, NF-κB, IRF3, IRF5, and SOCS3 protein bands were depicted in the immunoblot images, and (e) the densitometric quantification of the protein bands presented as a histogram (n = 3 per group). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. N: WB-F344 cells co-cultured with inactivated RAW264.7 cells; M: WB-F344 cells co-cultured with LPS (100 ng/mL)-activated RAW264.7 cells (referred to as LPS-RAW264.7); YGJ: WB-F344 cells co-cultured with LPS-RAW264.7 treated with Yiguanjian decoction; WIF-1: WB-F344 cells co-cultured with LPS-RAW264.7 treated with Wnt inhibitory factor-1.