Figure 2.
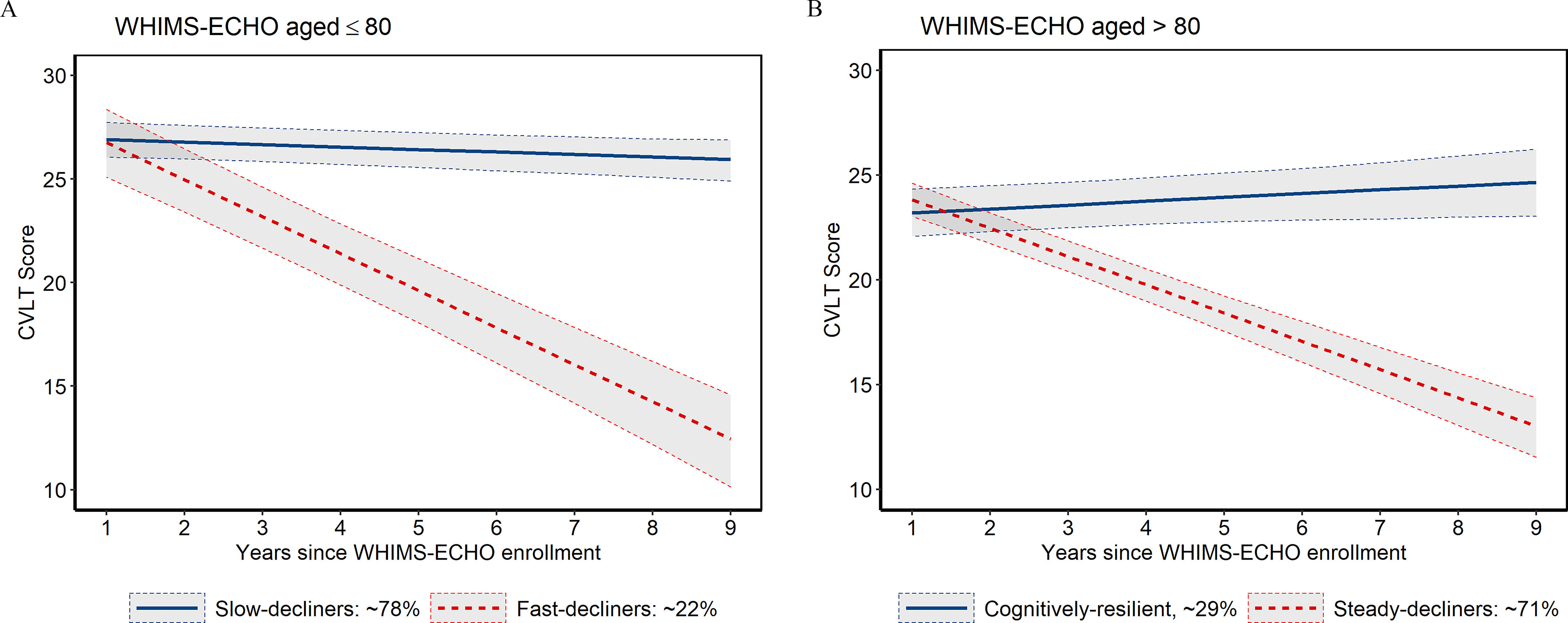
Median predicted CVLT trajectory over time by latent class in the WHIMS-ECHO cohort, stratified by age. (A) In women , the average rate of change in CVLT scores was (95% CI: , ; ) for the slow-decliner latent class (, according to the baseline LCMM) and (95% CI: , ; ) for the fast-decliner class (). (B) In women , the average rate of change in CVLT scores was 0.18/y (95% CI: , 0.36; ) for the cognitively resilient latent class (, according to the baseline LCMM) and (95% CI: , ; ) for the steady-decliner class (). Solid lines indicate the median predicted change in CVLT scores over time for women who were (A) 78 or (B) 84 years of age at WHIMS-ECHO enrollment. The predicted CVLT scores were estimated using baseline LCMMs with age at WHIMS-ECHO enrollment and follow-up time as the only predictors. Shaded regions denote 95% CI. Note: CI, confidence interval; CVLT, California Verbal Learning Test; LCMM, latent class mixed model; WHI-CT (HT), Women’s Health Initiative-Clinical Trial (Hormone Therapy); WHIMS-ECHO, Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study-Epidemiology of Cognitive Health Outcomes.
