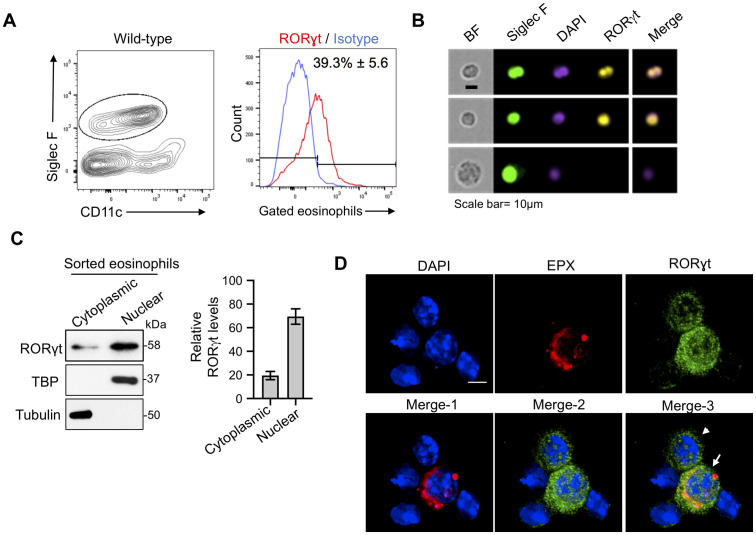
Fig 2. RORγt is expressed in lung eosinophils from mice with acute and allergic aspergillosis.
(A) Flow cytometry (allergy model). Allergic pulmonary aspergillosis was modeled as in Fig 1A. Lung cells were fixed, permeabilized and stained with anti-RORγt or isotype control. FACS plots are representative of 2 experiments, each with 4–5 mice per group. The means ± SE of RORγt-staining eosinophils combining each mouse experiment are shown next to the histogram. (B) Imaging flow cytometry (allergy model). As is Fig 2A, except lung cells were analyzed by imaging flow cytometry after staining for Siglec F, DAPI (nuclear stain) and RORγt. Shown are representative output images from >100 analyzed cells. BF; Bright field. Scale bar, 10μm. (C) Immunoblotting (allergy model). As in Fig 2A except eosinophils were purified by flow-sorting. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were prepared by cellular fractionation, resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with primary antibodies against RORγt, TATA-binding protein (TBP) and α-tubulin. TBP was used as nuclear and α-Tubulin as cytoplasmic controls, respectively. Left panel shows representative immunoblots. Right panel shows the means ± SD of the relative density from 2 immunoblots probed for RORγt. (D) Confocal microscopy (acute infection model). C57BL/6 mice were infected with 5 x 107 A. fumigatus conidia. Two days post-infection, cells were harvested by BAL, permeabilized, and stained for the eosinophil marker, EPX (red), RORγt (green) and DAPI (blue). Merge-1: DAPI + EPX; Merge-2: DAPI + RORγt; Merge-3: DAPI + EPX + RORγt. Scale bar = 5μm. The arrow points to an eosinophil while the arrowhead points to a presumed neutrophil. Both cells exhibit RORγt staining.