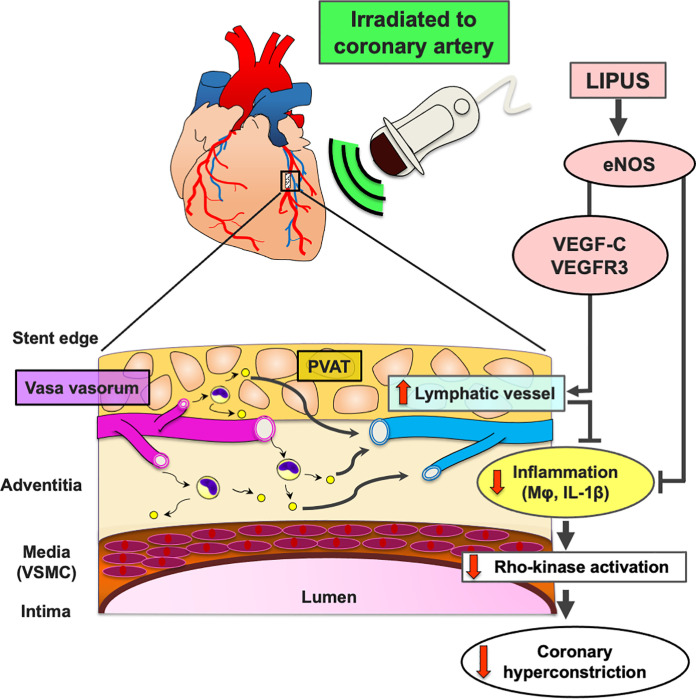
Fig 7. LIPUS ameliorates DES-induced coronary adventitial inflammation and resultant coronary hyperconstricting responses in pigs in vivo.
DES implantation induces coronary adventitial and PVAT inflammatory changes, including adventitial vasa vasorum augmentation, Mφ infiltration, and cytokine expressions in pigs in vivo. Importantly, cardiac lymphatic vessels act as a drainage for inflammatory changes, and thus impaired lymphatic function exacerbates adventitial inflammation, and subsequent medial VSMC hypercontraction through Rho-kinase activation (a central molecular switch of coronary artery spasm). In the present study, we were able to demonstrate that the LIPUS therapy enhanced coronary lymph-angiogenesis through up-regulations of eNOS and VEGF-C/VEGFR3, which prompted lymph transport speed for inflammatory cells (Mφ) and inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β). Mechanistically, the LIPUS therapy suppressed Rho-kinase activation and subsequent medial VSMC hypercontraction. DES = drug-eluting stent; Mφ = macrophage; PVAT = perivascular adipose tissue; VSMC = vascular smooth muscle cell; other abbreviations as in Figs 1–4.