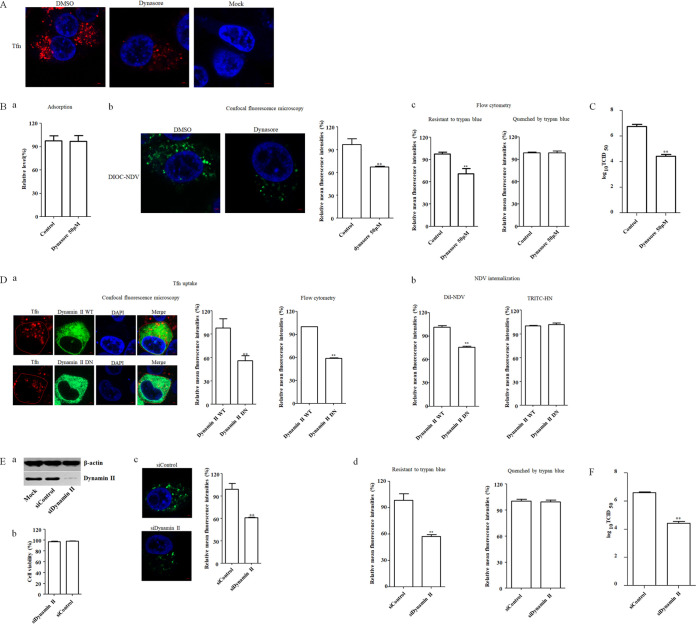
FIG 3.
NDV entry into HD11cells depends on dynamin. (A) Dynasore inhibited Tfn uptake. HD11 cells were treated with 50 μM dynasore or DMSO for 1 h at 37°C, followed by incubation with 10 μg/ml Tfn for 1 h at 4°C, and then shifted to 37°C for 1 h; after a wash with low-pH buffer, the cells were fixed and stained with DAPI. (B) Dynasore inhibited the internalization of NDV. HD11 cells were treated with the indicated concentration of inhibitors for 1 h at 37°C. The cells were then incubated with NDV F48E9 in the presence of inhibitors for 1 h at 4°C to allow for viral adsorption. DMSO was included as a negative control. Viral RNA was quantified by real-time RT-PCR (a). Alternatively, DiOC-labeled NDV F48E9 was adsorbed onto HD11 cells and then incubated with indicated concentrations of inhibitors for 1 h at 37°C to permit internalization. After a wash with low-pH buffer and quenching the green fluorescence of DiOC in the plasma membrane surface with trypan blue, the green fluorescence of internalized virus was determined by confocal fluorescence microscopy (b). Meanwhile, the treated cells were subjected to flow cytometry. Each cell sample was divided into two. One sample was subjected directly for the flow cytometric analysis, and another was treated with trypan blue (c). The fluorescence intensity which was resistant and quenched by trypan blue in inhibitor-treated cells was calculated relative to that of control cells (×100%). (C) Dynasore reduced the replication of NDV. HD11 cells were infected with NDV F48E9 at an MOI of 0.1 in the presence of the inhibitors at 37°C for 1 h. DMSO was included as a negative control. The cells were then washed with PBS and incubated in medium containing 5% FBS at 37°C. At 18 hpi, the viral titers in the culture supernatants of infected cells were determined. (D) Effects of dynamin II on Tfn uptake and NDV internalization. HD11 cells transfected with the EGFP-tagged WT or DN dynamin II were incubated with 10 μg/ml Tfn and DiI-labeled or unlabeled NDV F48E9 for 1 h at 4°C and then shifted to 37°C for 1 h. After a wash with low-pH buffer, the red fluorescence of Tfn in EGFP-positive cells was determined by confocal fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry, respectively (a). The red fluorescence of DiI-labeled NDV in EGFP-positive cells was determined by flow cytometry (b). In addition, the level of HN protein on the cell surface in unlabeled NDV-infected EGFP-positive cells was determined using anti-HN antibody via flow cytometry (b). (E) Dynamin II knockdown inhibited the internalization of NDV. HD11 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting dynamin (siDynamin II) or a control siRNA (siControl). The effect of siRNA knockdown on dynamin expression was determined by Western blotting (a). Cell viability upon siDynamin II and siControl transfection was assessed as described in the text (b). At 48 h posttransfection, the internalization assay was performed with DiOC-labeled NDV F48E9 as described above. The green fluorescence of DiOC that was resistant and quenched by trypan blue was determined by confocal fluorescence microscopy (c) and flow cytometry (d), respectively. (F) Dynamin knockdown reduced the replication of NDV. HD11 cells were transfected with siDynamin II or siControl. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were infected with NDV F48E9 at an MOI of 0.1, and the viral titers in the culture supernatants of infected cells were determined at 18 hpi. The bars represent means ± the SD. Data were analyzed by using the Student t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).