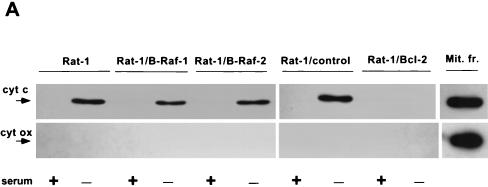
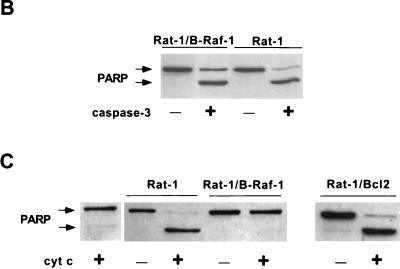
FIG. 8.
Effect of B-Raf overexpression on cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation. (A) Wild-type Rat-1 cells (Rat-1), transfected Rat-1 cells overexpressing B-Raf (Rat-1/B-Raf-1 and -2) or Bcl-2 (Rat-1/Bcl-2), and transfected Rat-1 cells that fail to overexpress B-Raf (Rat-1/control) were maintained in the presence of serum or deprived of growth factors for 24 h. Equal amounts of cytosolic proteins were then immunoblotted for cytochrome c (cyt c) and cytochrome oxidase subunit II (cyt ox), along with similar amounts of mitochondrial fraction (Mit. fr.) of Rat-1 cells maintained in serum as a positive control. The positions of cytochrome c and cytochrome oxidase are indicated by arrows. (B) Cytosols from Rat-1 and Rat-1/B-Raf cells were combined with purified, active His6-tagged human caspase-3 and intact HeLa cell nuclei and then incubated for 1 h at 37°C. The reaction mixture was used for immunoblot analysis to measure the cleavage of the caspase-3 substrate PARP. Intact PARP (116 kDa) and the cleaved fragment (85 kDa) are indicated by arrows. (C) Activation of caspase-3 was induced by the addition of cytochrome c to cytosols from nonapoptotic Rat-1, Rat-1/B-Raf, and Rat-1/Bcl-2 cells maintained in the presence of serum. Reaction mixtures were combined with intact HeLa cell nuclei, and the cleavage of PARP was assayed by immunoblot analysis. Lane 1 is a control in which cytochrome c was added to nuclei without cytosolic extract. The results are representative of at least three similar experiments.