Figure 1.
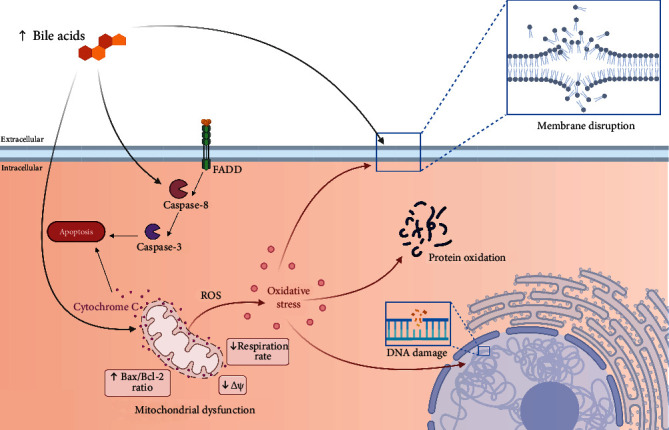
Cytotoxicity mechanisms induced by bile acids (BA). BA can induce membrane disruption by an alteration of stability and composition due to their steroid structure. Moreover, BA activate the caspase pathway in a Fas receptor-dependent mechanism (FADD), triggering cellular apoptosis. In addition, BA affect the mitochondrial function by (1) decreasing the rate of respiration, (2) diminishing the membrane potential, (3) increasing the permeability transition pore facilitating the translocation of cytochrome C and contributing to apoptosis, and (4) inducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. The increased ROS levels lead to cellular oxidative stress capable of inducing DNA damage, protein oxidation, and lipid peroxidation, contributing to cellular membrane damage. All these mechanisms impair cellular viability.
