Figure 13.
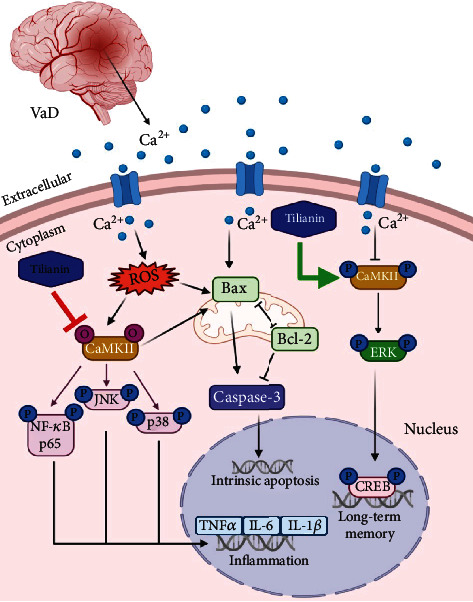
Potential neuroprotective mechanism of tilianin against VaD via the p-CaMKII and ox-CaMKII signaling pathways as established in the present study. Tilianin promoted long-term memory-related signaling pathways and inhibited apoptosis, inflammatory reaction, and oxidative stress levels via CaMKIIα. Bax: B cell lymphoma-2 associated X protein; Bcl-2: B cell lymphoma-2; CaMKII: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; caspase: cysteine-dependent aspartate-specific proteases; CREB: cAMP-response element-binding protein; ERK: extracellular regulated protein kinases; IL-1β: interleukin-1 beta; IL-6: interleukin-6; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-B; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; VaD: vascular dementia.
