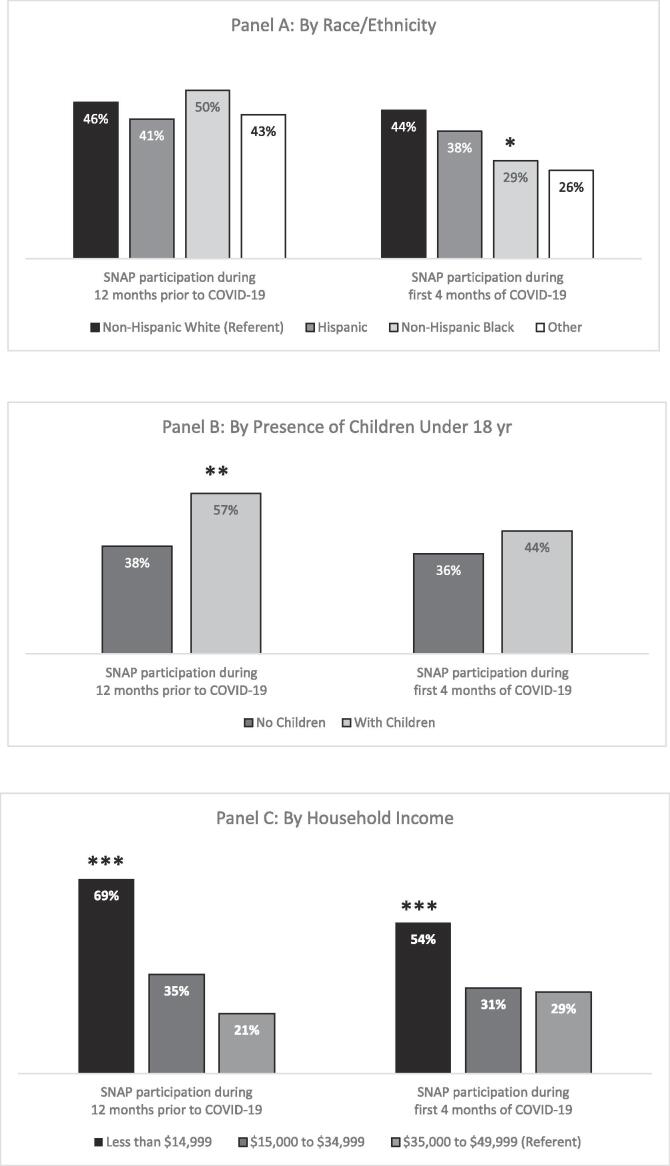
Fig. 2.
Adjusted Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) Participation Before and After COVID-19 Pandemic Onset among Low-Income (< $50,000) Food Insecure Households.
Note: Self-reports of SNAP participation in the 12 months prior to and during the 4 months after onset of the COVID-19 pandemic were used to calculate SNAP participation rates. Estimates presented are based on multivariate regression models (see Appendix 1) predicting SNAP participation among different income groups, adjusting for age, sex, and race/ethnicity of the respondent, household income, household size, an indicator for households with children, food pantry use, and score on the USDA food insecurity module indicating the number of affirmative answers to the USDA six-item food security questions. * Post-pandemic onset, non-Hispanic Black households participated in SNAP at significantly lower rates than did non-Hispanic White households (p < 0.05) (Panel A). ** In the year prior to the pandemic, households with children participated in SNAP at significantly higher rates than did households without children (p < 0.01) (Panel B). *** Households in the lowest income group participated in SNAP at significantly higher rates than did households in the highest income group both prior to and since the onset of the pandemic (p < 0.001) (Panel C).