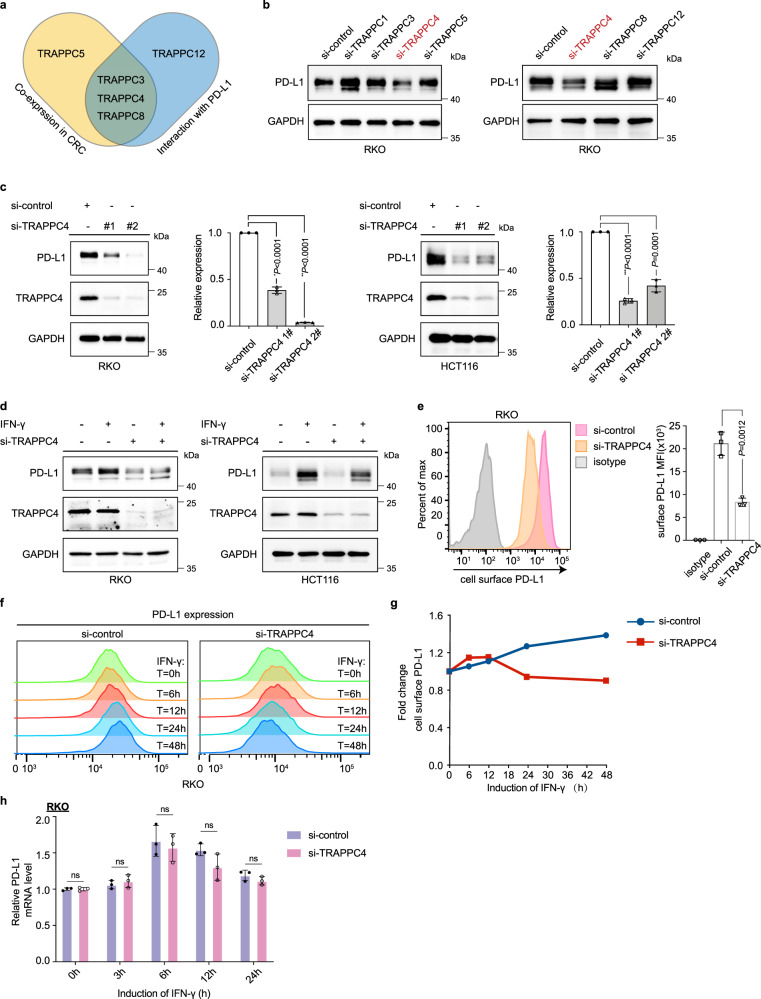
Fig. 2. TRAPPC4 is identified as a positive regulator of PD-L1.
a Venn diagram showing the TRAPP subunits that positively correlated with PD-L1 protein based on the proteogenomic analysis and the TRAPP subunits that interacted with PD-L1 based on the mass spectrometry analysis. b Immunoblot showing PD-L1 protein levels in RKO cells transfected with siRNAs targeting different subunits of the TRAPP complexes. c Immunoblot for multiple CRC cells treated with control siRNAs or TRAPPC4 siRNAs. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Values indicate means ± SD of the relative gray values of the indicated blots. (*P = 6.9e-6, **P = 3.06e-11, ***P = 7.7e-7). d Western blot showing the effect of TRAPPC4 depletion on IFN-γ-induced PD-L1 expression in the indicated cells. e PD-L1 expressed on cell surface detected by flow cytometry in RKO cells transfected TRAPPC4-specific siRNA versus the control siRNA. Values indicate means ±SD of the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). f, g TRAPPC4 knockdown or control siRNA-transfected RKO cells were induced with IFN-γ at the indicated time points and cell surface PD-L1 was detected using flow cytometry. h mRNA levels of PD-L1 in TRAPPC4 knockdown or control RKO cells, with or without the induction of IFN-γ at different time points. Values indicate means ±SD. ns, not significant. Experiments in b–h were performed three times independently with similar results. Statistical differences were determined using a two-sided Student’s t test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.