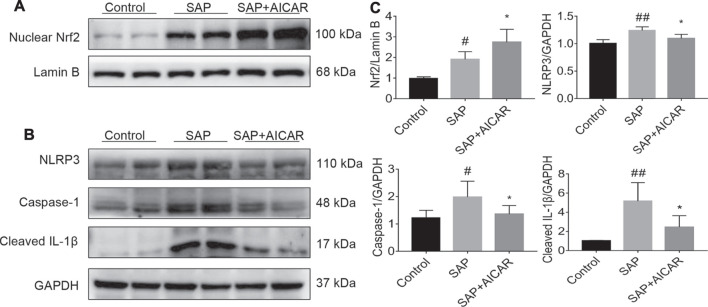
FIGURE 4.
The effects of AICAR on the activation of the AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway and inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the liver tissues of sodium taurocholate-induced SAP rats. 7–8 week-old wild-type male SD rats were randomly divided into three groups: the control group (control, n = 10) was treated with sham operation and injected with 0.9% normal saline; the severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) group (n = 10) was infused with 3% sodium taurocholate (0.1 ml/100 g); and the AMPK agonist (AICAR) group (n = 8) received intraperitoneal injection of AICAR (400 mg/kg) 1 h before the operation. (A) The levels of nuclear accumulation of Nrf2 in liver tissues of each group were detected by Western blot analysis. For the internal control, Lamin B was used. (B) The protein expression levels of NLRP3, caspase-1, and cleaved IL-1β in liver tissues were measured by Western blot using anti-NLRP3, anti-caspase-1 and anti-cleaved IL-1β antibodies. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (C) Relative band densities were quantified using VisionWorks imaging software, and the results are expressed in the histogram. Data are presented as the mean ± SD obtained from three independent experiments. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, #### p < 0.0001 vs control group; * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs. SAP group.