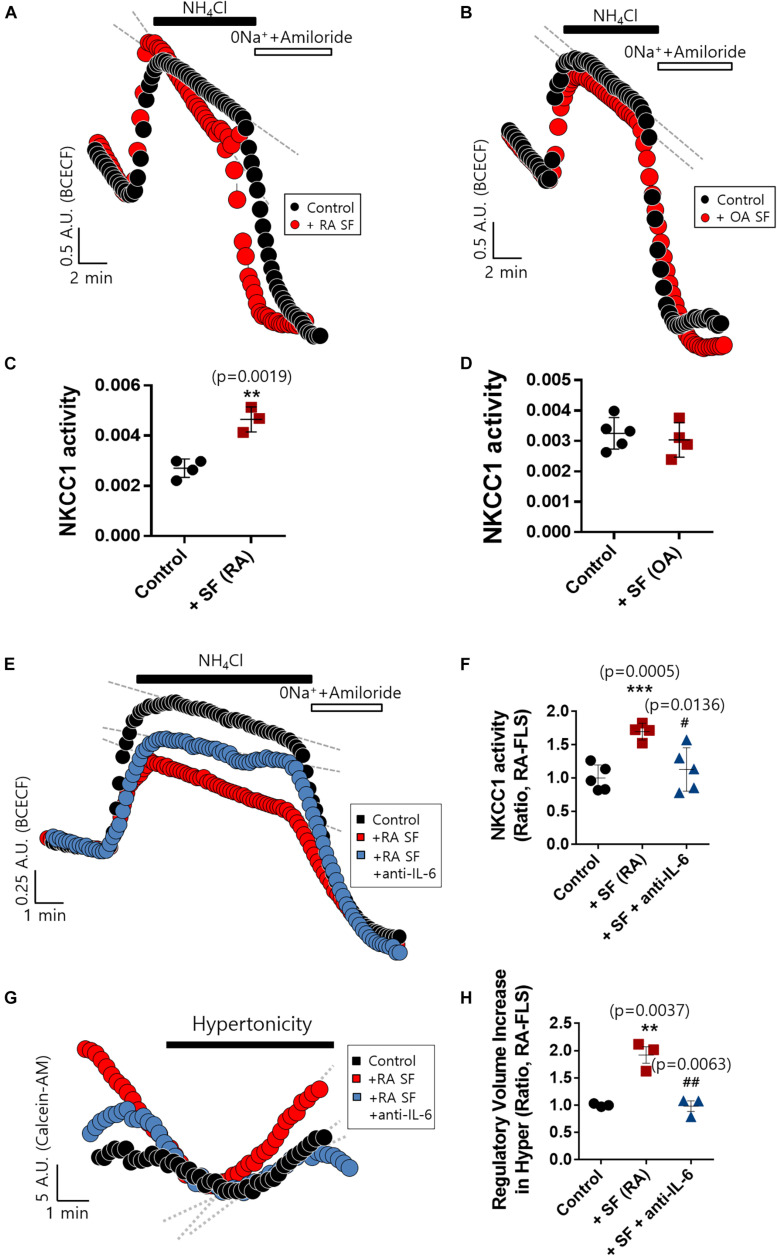
FIGURE 5.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fluid enhanced sodium–potassium–chloride cotransporter1 (NKCC1) activity and interleukin (IL)-6 antibody blocked the effect of RA synovial fluid in RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLS). NKCC1 activity was measured using the membrane of a Boyden Transwell chamber with pretreatment with (A) RA and (B) osteoarthritis (OA) synovial fluid for 6 h in RA-FLS. The bars represent the mean ± SEM of NKCC1 activity with or without (C) RA [n = 4, **p < 0.01, *: Control vs + SF (RA)] and (D) OA synovial fluid in RA-FLS. (E) NKCC1 activity by the stimulation of RA synovial fluid with or without 5 μg/ml anti-IL-6 antibody for 6 h in RA-FLS on the membrane of Boyden Transwell chamber. (F) The bars represent the mean ± SEM of NKCC1 activity [n = 5, ***p < 0.001, and #p < 0.05, *: Control vs + SF (RA), #: + SF (RA) vs + SF + anti-(IL)−6]. (G) Volume changes in RA-FLS on stimulation with a hypertonic solution (400 mOsm/L). RA synovial fluid was pre-treated with 5 μg/ml anti-IL-6 antibody for 1 h and then stimulated to RA-FLS on the membrane of Boyden transwell chamber for 6 h. (H) The bars represent the mean ± SEM of volume changes. Hypertonic solution (hyper) [n = 3, **p < 0.01 and ##p < 0.01, *: Control vs + SF (RA), #: + SF (RA) vs + SF + anti-(IL)−6].