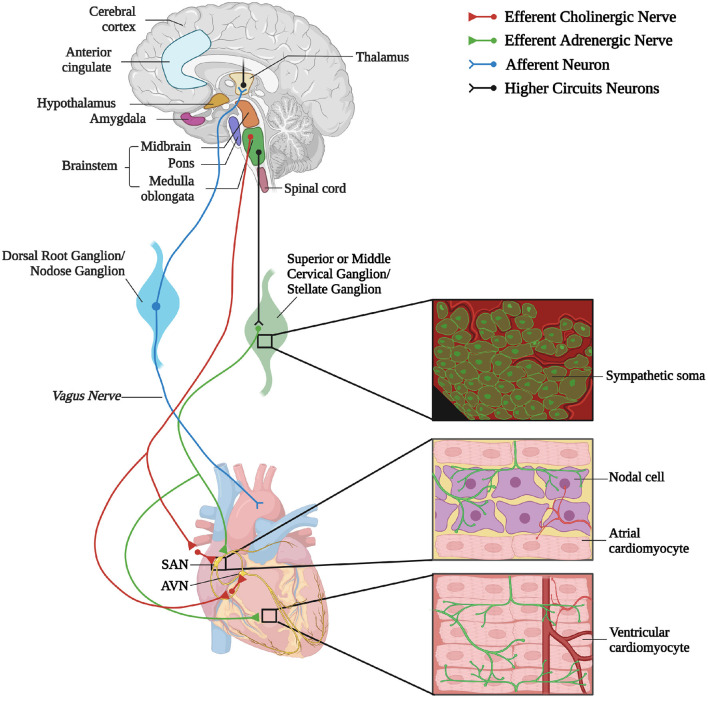
Figure 1.
The complex neuronal circuitries underlying bidirectional “brain–heart” connection. Schematic representation of the “brain–heart axis.” Different regions of the brain, belonging to the CAN process precise orders which are transmitted, through efferent preganglionic fibers, to both sympathetic (adrenergic) and parasympathetic (cholinergic) cardiac ganglia. While PSN processes mainly innervate the SAN and the AVN, SNs invade the conduction system and the working myocardium. The cardiac muscle is also innervated by intrinsic neurons (INS) and cardiac sensory neurons, whose cell bodies organize into the dorsal root ganglion and nodose ganglion, and their afferent fibers project to different areas of the brain (created with BioRender.com).