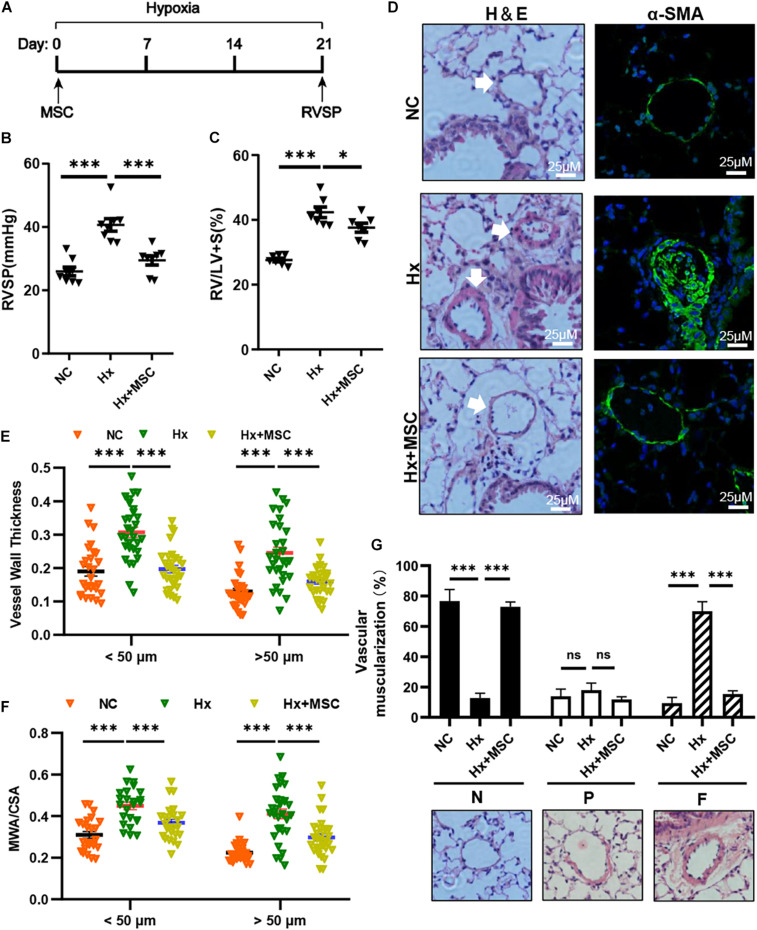
FIGURE 1.
MSCs attenuate the development of hypoxia (Hx)-induced PH in mice. (A) Protocol for the administration of MSCs to Hx-challenged mice. (B,C) Effect of MSC administration on RVSP and the RV/LV + S ratio in hypoxia-induced PH mice. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (n = 7). (D) Representative hematoxylin and eosin-stained lung sections and immunofluorescence images of α-SMA (green) expression in Hx-induced mice treated with MSCs. Scale bars: 25 μm. (E) Quantification of the vessel wall thickness of the pulmonary artery. ∗∗∗P < 0.001. (F) Quantification of the ratio of the medial wall area (MWA) to the total vessel cross sectional area (CSA). ∗∗∗P < 0.001. (G) Proportion of non- (N), partially (P), or fully (F) muscularized PAs in the total counted PAs. A total of 30–50 vessels were analyzed in each mouse (n = 4–6), ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was evaluated by t-tests.