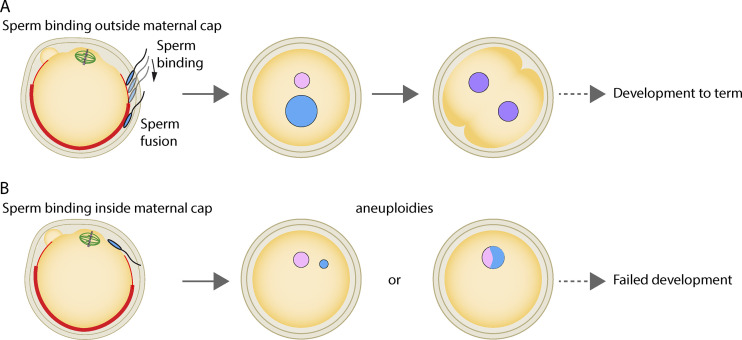
Figure 1.
Sperm binding is favored outside the maternal actin cap for successful embryo development. The density of microvilli (bold red area) increases away from the metaphase II egg spindle, in correlation with more important Juno and CD9 staining patterns. (A) Sperm binding outside the maternal actin cap. A sperm bound in the transition zone (lighter red area), with fewer microvilli and more lamellipodia-like structures, will move toward the denser microvilli area where it will fuse to the egg, preventing its elimination during second polar body extrusion. This mechanism favors correct ploidy of the zygote and its development to term. (B) Sperm binding inside the maternal actin cap. Binding and fusion in the microvilli-depleted region will produce aneuploid zygotes with reduced chances of successful development. Maternal chromosomes appear in pink, paternal ones in blue, parental genome mixing in purple, and spindle microtubules in green.