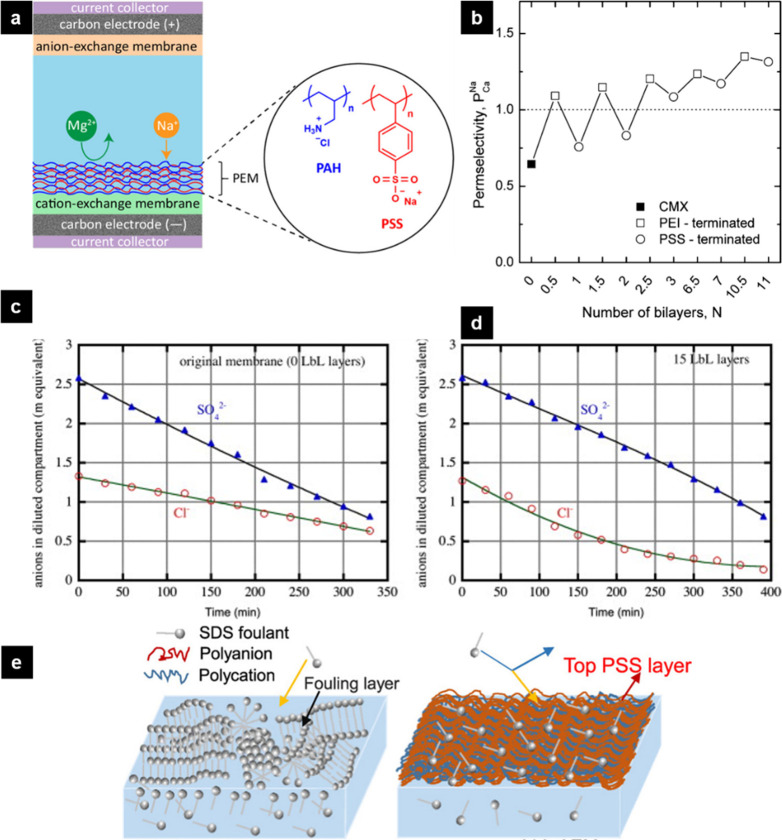
Figure 5.
(a) Illustration of a PEM application on a standard cation-exchange membrane to achieve Na+/Mg2+ selectivity in capacitive deionization. PAH and PSS stand for poly(allylamine hydrochloride) and poly(styrenesulfonate), respectively. Reproduced with permission from ref (183). Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society. (b) Trend in permselectivity (P) as a function of the type of the terminating layer. CMX and PEI stand for standard cation-exchange membrane and poly(ethylenimine), respectively. The empty squares represent the PEI-terminated and the empty circles represent the PSS-terminated multilayers. Reproduced with permission from ref (184). Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society. (c) Change in the anion concentration in time in the diluted compartments of the experiments with the bare membrane and (d) the membrane with 15 layers. (c and d) Reproduced with permission from ref (185). Copyright 2013 Elsevier. (e) Comparison of the bare (left) and the PEM-coated (right) membranes for SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) fouling. Reproduced with permission from ref (186). Copyright 2018 Elsevier.