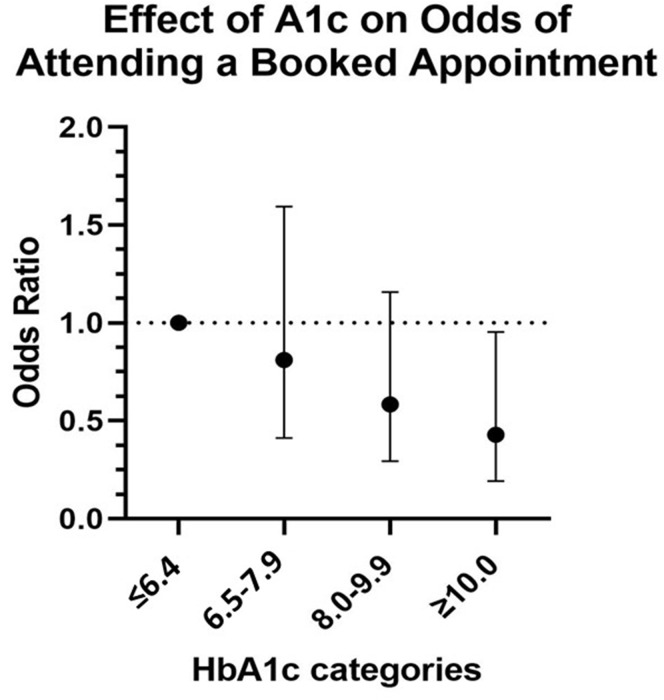
Fig. 3.
Effect of HbA1C on the odds of attending a booked appointment after the outreach intervention. Outreach was attempted for 787 patients who canceled an appointment for diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic. Outcome was defined as booking and keeping an appointment after the outreach initiative. Patients with a higher HbA1C level were less likely to keep their appointment (odds ratio = 0.87 for each 1.0% increase in the HbA1C level, P for trend = .01). HbA1C is reported in quartiles of ≤6.4% (≤46 mmol/mol), 6.5% to 7.9% (48-63 mmol/mol), 8% to 9.9% (64-85 mmol/mol), and ≥10% (≥86 mmol/mol). HbA1C = hemoglobin A1C.