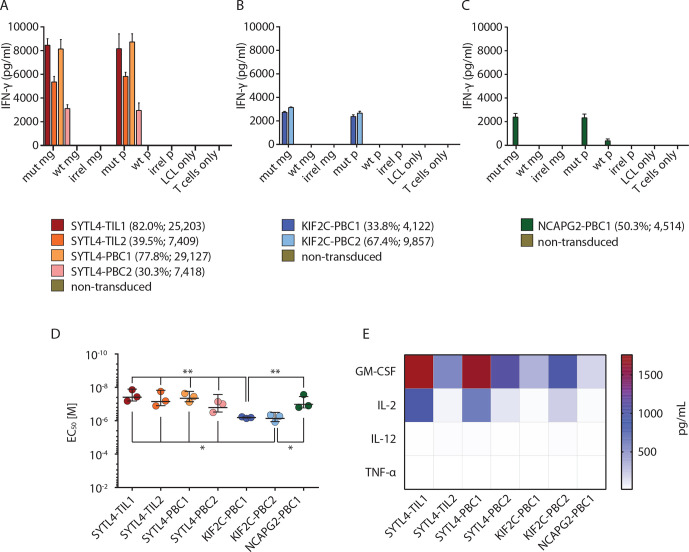
Figure 2.
High specificity and strong functional performance of identified TCRs in vitro. (A–C) Secretion of IFN-γ by CD8+ T cells transduced with TCRs specific for SYTL4S363F (A), KIF2CP13L (B), and NCAPG2P333L (C) after coculture with LCL-1-presenting neoantigens and respective WT counterparts at effector to target (E:T)=1:1 is shown. LCL-1 transduced with MGs encoding for fragments of mut sequence (mut MG), WT sequence (WT MG) or irrelevant sequence (irrel MG) were compared with peptide pulsed LCLs (mut P, WT P, irrel P; 1 µM peptide). IFN-γ secretion in supernatants was investigated by ELISA assay. Bars represent average reads from three duplicates; error bars represent SD transduction efficiencies; and Mean Fluorescent Intensity (MFI) values are indicated below the graphs. (D) Comparison of functional avidity of neoantigen-specific TCRs, calculated as EC50 of cognate mutated peptide. IFN-γ secretion was assessed on supernatants, and a non-linear curve was fit to determine the EC50 value. EC50 values deriving from three different experiments were depicted for each TCR. Bars in the graph represent the mean value, and SD significance is calculated with one-way analysis of variance and Tukey multiple comparison test (*p≤0.05, **p≤0.01). (E) Assessment of multicytokine secretion of TCR-transduced T cells on coculture with LCL-1 pulsed with mutated peptides. All experiments were performed at least with three different sets of transduced T cells derived from two different healthy donors. EC50, half maximal effective concentration; IFN, interferon; LCL, lymphoblastoid cell line; MG, minigene; mut, mutant; TCR, T-cell receptor; WT, wild type.