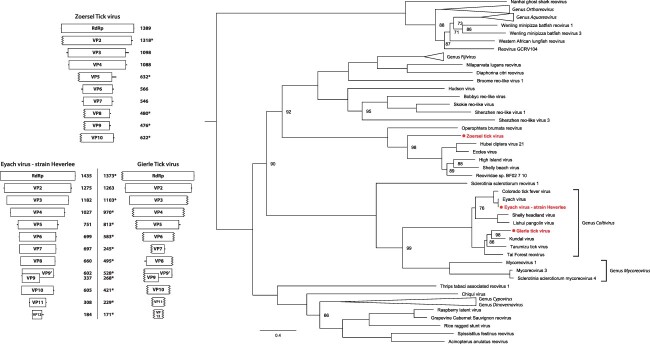
Figure 4.
Reovirus phylogeny and genome organization. Left: genome organization of Eyach virus strain Heverlee, Gierle tick virus, and Zoersel tick virus, with segment lengths drawn according to scale. Ribbed lines indicate incomplete genome ends. The deduced amino acid length of all proteins is shown next to the corresponding segments. *Incomplete ORFs. Right: maximum-likelihood tree based on the protein sequence of the RdRp of all the (putative) members of the subfamily Spinareovirinae for whom such a sequence is available, shows Eyach virus strain Heverlee and Gierle tick virus clustering within the genus Coltivirus, with Gierle tick virus representing a novel species. Zoersel tick virus forms a separate branch within the subfamily, alongside several yet unclassified viruses. The scale bar indicates the number of amino acids substitutions per site. The numbers at the node indicate the bootstrap support for each node, based on 1,000 replicates. Only values <100 are shown. All used accession numbers are provided in Supplementary Table S4.