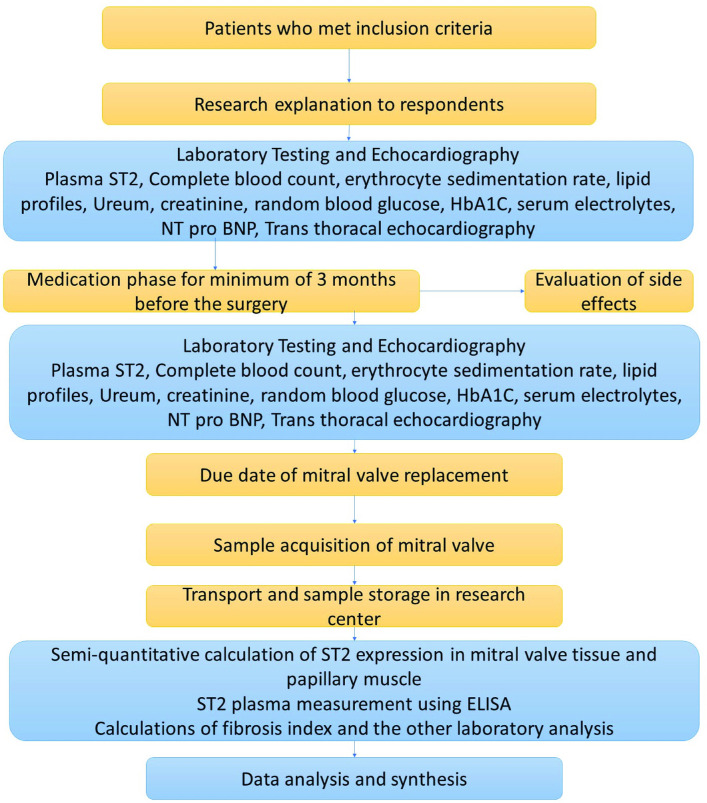
Figure 1.
Hypothesis. Molecular mimicry is a defence mechanism of group A Streptococcus to avoid immune cells. This mechanism allows immune cells to generate autoimmunity against protein the lining of endothelial cells and causing chronic inflammation and valvular damage. Continuous process of chronic inflammation leads to valvular thickening and fibrosis, which is mediated by the angiotensin II. Angiotensin II increase TGF-β expression and cause IL-33 to bind with sST2, and subsequently cause damage and fibrosis to the valvular tissue even more, which later will end with rheumatic heart failure. ACEI is hypothesised to counteract these processes by decreasing angiotensin II conversion from angiotensin I. ACEI, ACE inhibitor; IL, interleukin; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β.