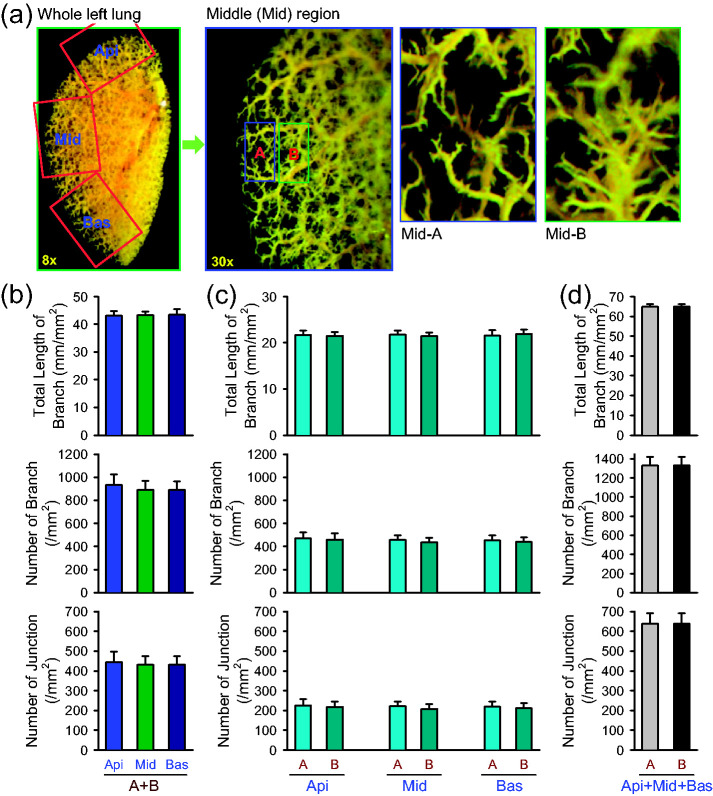
Fig. 2.
Comparison of angiography parameters in different peripheral regions of mouse lung. (a) Representative angiograph images of the whole left lung at 8× magnification and the middle (Mid) peripheral region of the left lung at 30× magnification (left panels). Enlarged angiograph images of the labeled middle (Mid) region (30×) depicting the most peripheral region (Mid-A) and the adjacent region (Mid-B). (b–d) Summarized data (mean±SE, n=6) showing the total length of lung vascular branches (upper panels), the number of lung vascular branches (middle panels) and the number of lung vascular branch junctions (lower panels) per square millimeter from the selected apical (Api), middle (Mid), and basal (Bas) lung areas (b), the selected most peripheral areas (A) and adjacent peripheral areas (B) in the Api, Mid, and Bas lung regions (c), and the combined (A+B) peripheral areas in the Api, Mid and Bas lung regions (d) from normal female and male mice.