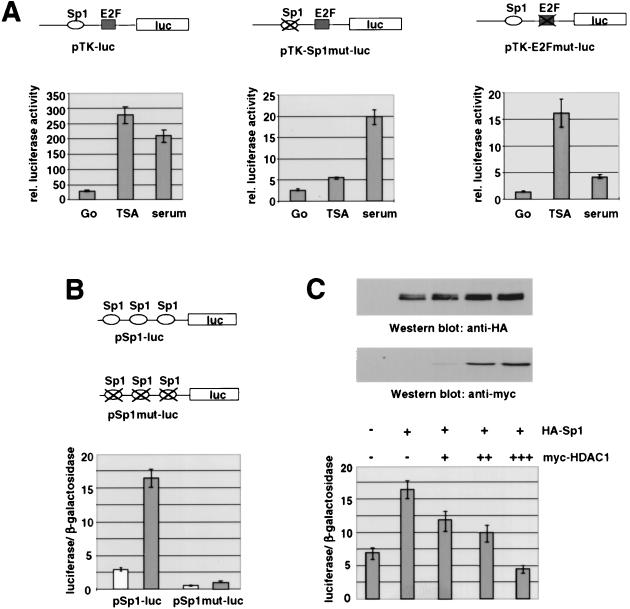
FIG. 1.
Sp1 binding sites can mediate transcriptional activation by TSA. (A) The Sp1 binding site is required for activation of the murine TK promoter by TSA in resting Swiss 3T3 cells. Serum-deprived cells containing the chromosomally integrated luciferase reporter genes pTK-luc, pTK-E2Fmut-luc, and pTK-Sp1mut-luc were incubated for 20 h either with TSA (80 ng/ml) or fresh medium supplemented with 20% fetal calf serum. Data are means and standard deviations from three independent experiments. rel., relative. (B) 293 cells were transiently transfected with a reporter plasmid containing three Sp1 consensus sites (pSp1-luc) or a construct bearing three mutated Sp1 sites (pmtSp1-luc) together with the control vector pCMVβGal. In each transfection experiment half of the cells were treated with TSA (100 ng/ml) for 20 h. Luciferase activities of untreated cells (white bars) and TSA-treated cells (gray bars) are depicted relative to the respective β-galactosidase activities. (C) pSp1-luc was transfected together with pCIneo, pCIneoHA-Sp1wt, and pCIneoHA-Sp1wt in combination with increasing amounts of pCIneomyc-HDAC1 (0.25, 0.75, and 1.25 μg). Luciferase activities are depicted relative to the respective β-galactosidase activities. Expression levels of epitope-tagged Sp1 and HDAC1 were analyzed on Western blots with HA-specific and Myc-specific antibodies.