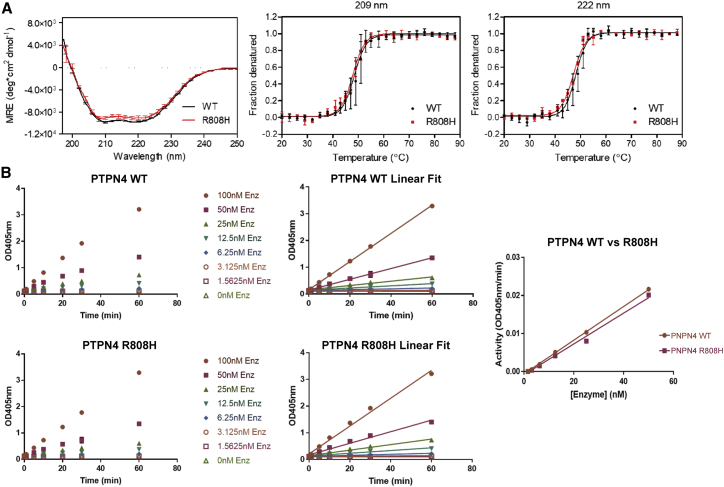
Figure 5.
Biochemical characteristics and phosphatase activity of variant p.Arg808His PTPN4
(A) Left panel: far-UV CD spectra of PTPN4 in 20 mM sodium phosphate (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl. The three replicates are plotted as an average. Error bars represent SD. The spectra of wild-type (WT) and R808H are essentially identical, which indicates that they have very similar secondary structure compositions. Middle and right panels: thermal denaturation of PTPN4 in 20 mM sodium phosphate (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl monitored by mean molar ellipticity per residue (MRE) at 209 and 222 nm. Error bars represent the SD of three replicates. For visualization purposes, not every data point is shown. The data were fit to a Boltzmann sigmoid using Prism. The R808H variant does not significantly affect the unfolding temperature (209 nm: p = 0.55; 222 nm: p = 0.30) or the cooperativity of unfolding (209 nm: p = 0.17; 222 nm: p = 0.19) of PTPN4. (B) Saturation kinetics of wild-type and variant PTPN4. His-tagged versions of the PTPN4 protein segments comprising the two catalytic domains containing WT and p.Arg808His variant sequences were expressed in bacteria and purified using nickel affinity chromatography. Equal amounts of WT and variant proteins were used to evaluate enzyme kinetics. The rate of hydrolysis of substrate (dNPP) is plotted against increasing substrate concentration. Data were fitted to the Michaelis-Menten equation.