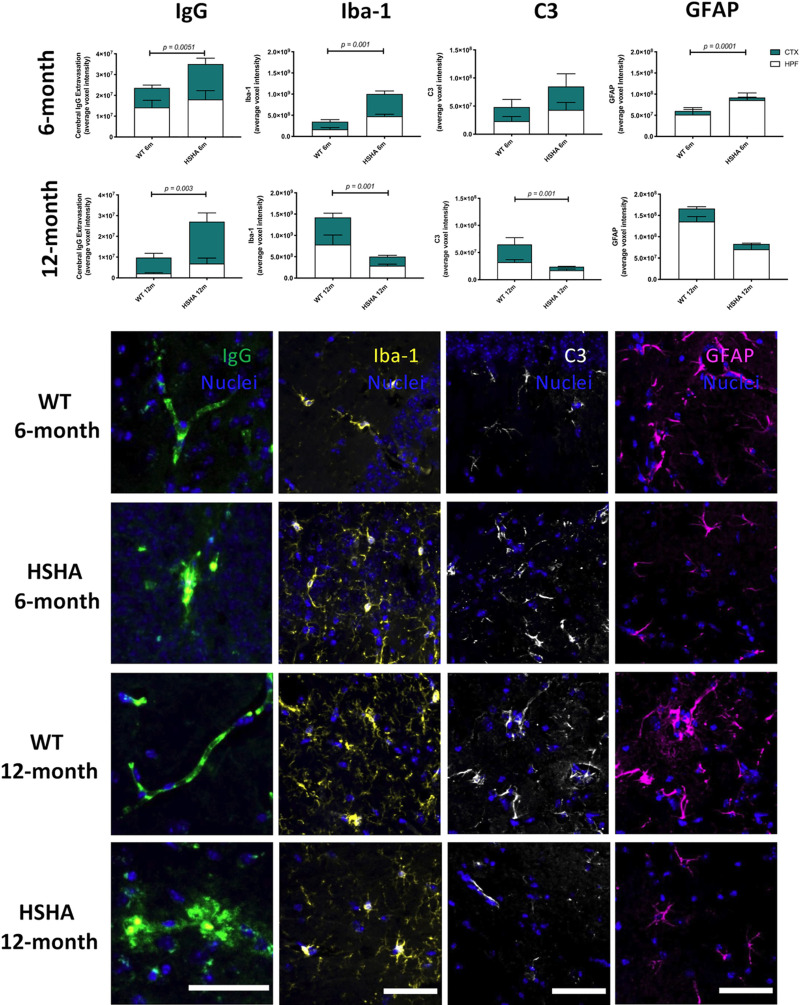
Fig 5. Three-dimensional confocal immunomicroscopy analysis of markers of cerebral capillary integrity, microglial activation, and astrocytic immunoreactivity.
Increased cerebral capillary permeability, activated microglia, A1 reactive astrocytes, and activated astrocytes were assessed by the quantitative immunoreactivity of cerebral extravasation of plasma protein IgG, Iba-1, C3, and GFAP, respectively, in the cerebral CTX and HPF of HSHA mice and their age-matched WT controls at 6 (A–D) and 12 months (E–H) of age. The latter frames, which are representative confocal immunomicrographs of IgG (green), Iba-1 yellow), C3 (white), and GFAP (magenta), are presented (nuclei are shown as blue; scale bar = 50 μm). Statistical significance between each strain and age were tested by an unpaired t test with Welch correction testing for nonequivalence of standard deviations. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4–12; p-values only indicated for significance). The data underlying Fig 5 A–H can be found in S1 Data. CTX, cortex; C3, complement component 3; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; HPF, hippocampal formation; HSHA, hepatocyte-specific human amyloid; Iba-1, ionised calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1; IgG, immunoglobulin G; WT, wild-type.