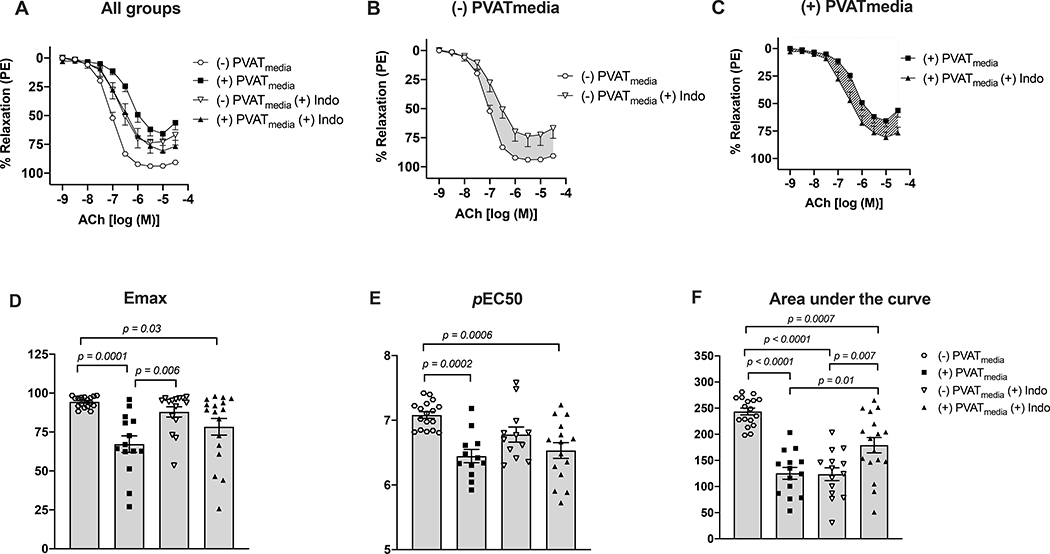
Figure 1. Effects of COX inhibition on ACh-induced relaxation in uterine arteries exposed to PVAT-derived factors in pregnant rats.
(A) All treatments; (B) Concentration-response curves to ACh in the presence or absence of indomethacin (no PVATmedia added). Grey shaded area indicates a reduction in ACh-induced relaxation in response to indomethacin; (C) Concentration-response curves to ACh in the presence or absence of indomethacin (PVATmedia added). Pattern-filled area indicates an increase in ACh-induced relaxation in response to indomethacin; (D) Maximum responses (Emax) to ACh for all concentration-response curves; (E) Negative logarithm of EC50 (pEC50) for all concentration-response curves; (F) Area under the curve for all concentration-response curves. Values are mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. ACh, acetylcholine; COX, cyclooxygenase; PVATmedia, perivascular adipose tissue conditioned media.