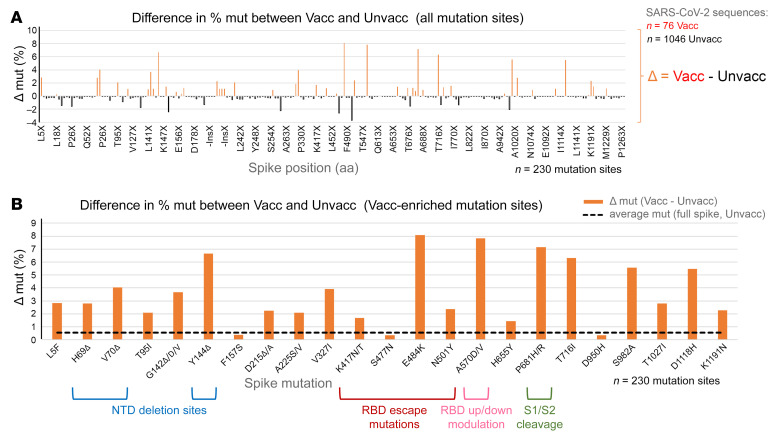
Figure 3. Site-specific spike mutation analysis in SARS-CoV-2 vaccine breakthrough sequences compared with unvaccinated matched controls.
(A) Comparison of site-specific amino acid mutation (mut) frequencies in spike in 76 vaccine breakthrough sequences (Vacc) compared with 1046 unvaccinated matched controls (Unvacc) from the same cohort. The Wuhan-Hu-1 sequence served as reference to call mutations per site, and all spike mutation sites of the study sequences are shown along the x axis according to their spike position (n = 230). The mirror plot displays differences of mutation frequencies between Vacc and Unvacc groups; orange bars (top) refer to higher mutation rates in Vacc sequences, whereas black bars (bottom) refer to higher mutation rates in Unvacc matched controls. (B) Enrichment of spike mutations in SARS-CoV-2 vaccine breakthrough sequences. All sites with greater spike mutation rates in Vacc compared with Unvacc controls are shown; sites with unique occurrences of mutations in breakthrough cases were disregarded. Mutation sites in the spike NTD, RBD, the C-terminal S1 region affecting RBD, and S1/S2 interface region that have been associated with VOCs, neutralization immune escape, and/or affecting important biological functions of the virus are highlighted. The dashed black line indicates the average mutation frequency across all spike residues in the unvaccinated control data set compared with Wuhan-Hu-1 as reference (n = 1046).