Figure 1.
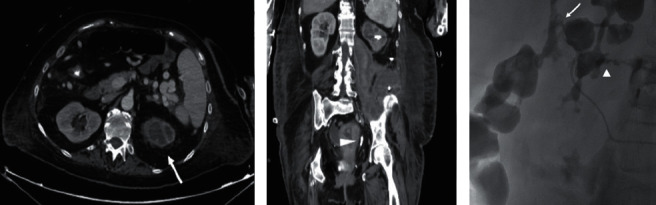
(a) Postcontrast CT images showed hypoperfusion of the left kidney with thinning of the cortex; dilatation of the left kidney excretory system with a “bear's paw sign” is also depicted suggesting diagnosis of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (arrow); (b) postcontrast coronal reconstruction demonstrated ureteral stone (arrowhead) in the distal tract of the left ureter without significant dilatation of the proximal tract; (c) oblique projection pyelography after puncture of the inferior calix of the left kidney demonstrated leakage of contrast media with a double fistulous path form the pelvis directed anteriorly to the left colon (arrow) and posteriorly to the collection in the retroperitoneal collection (arrowhead).
