FIG. 6.
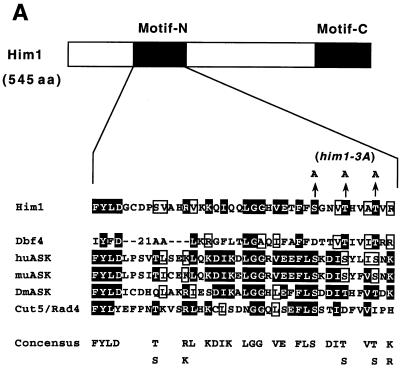
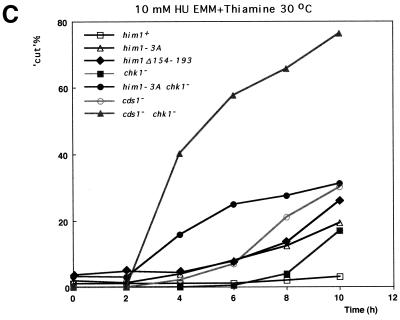
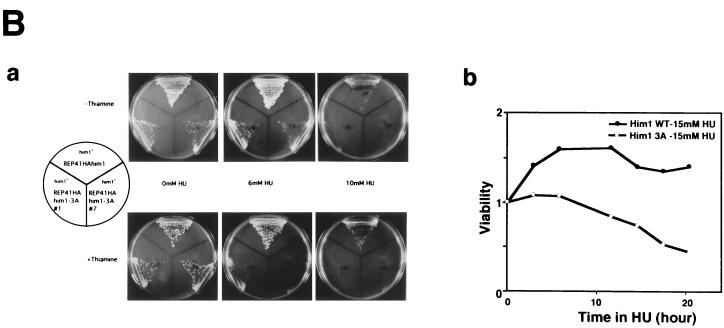
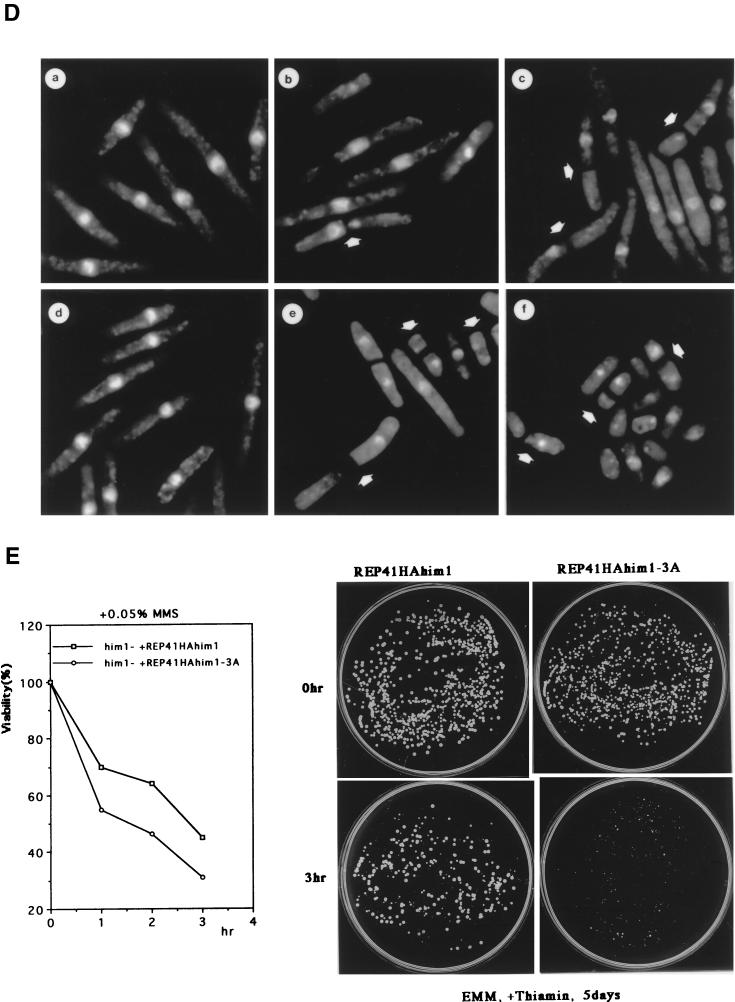
An alanine substitution mutant of Him1 protein exhibits sensitivity to HU and DNA-damaging agents. (A) Alignment of motif N conserved in Him1 and regulatory subunits (ASK) for Cdc7-related kinases from higher eukaryotes (41) as well as in fission yeast Cut5 protein (59). Three conserved serine/threonine residues mutated to alanine are indicated. Residues conserved in more than three members or those not identical but with similar functionality are shown as white or boxed letters, respectively. (B) Effect of HU on growth of him1− cells carrying a plasmid expressing wild-type or 3A mutant him1 (two independent clones); growth on plates (a) or survival rate in liquid culture (b). Plates shown are with (lower panel) or without (upper panel) thiamine. (C) Appearance of cut-like cells in HU-treated him1Δ154-193 and him1-3A mutant cells. Various vegetatively growing transformants or mutant strains (5 × 106 cells/ml) were grown in the presence of 10 mM HU and thiamine. Aliquots were sampled every 2 h to count the number of cut cells under the fluorescence microscope. (D) Cut-like morphology of him1− transformants or deletion strains. Cells arrested with HU for 8 h described in panel C were stained with DAPI and were examined by fluorescence microscopy. (a) him1− cells plus pREP41HAhim1; (b) him1− cells plus pREP41HAhim1-3A; (c) cds1− cells; (d) him1− chk1− pREP41HAhim1; (e) him1− chk1− cells plus REP41HAhim1-3A; (f) cds1− chk1−. White arrows indicate cut-like cells. (E) Growth recovery from DNA damage in him1− cells expressing Him1-3A. Vegetatively growing cells (5 × 106 cells/ml) were treated with MMS in the presence of thiamine, and aliquots were sampled every hour. One thousand cells were plated on EMM to examine survival of DNA damage. Survival curve (left panel) and colony formation assay (right panel) are shown.