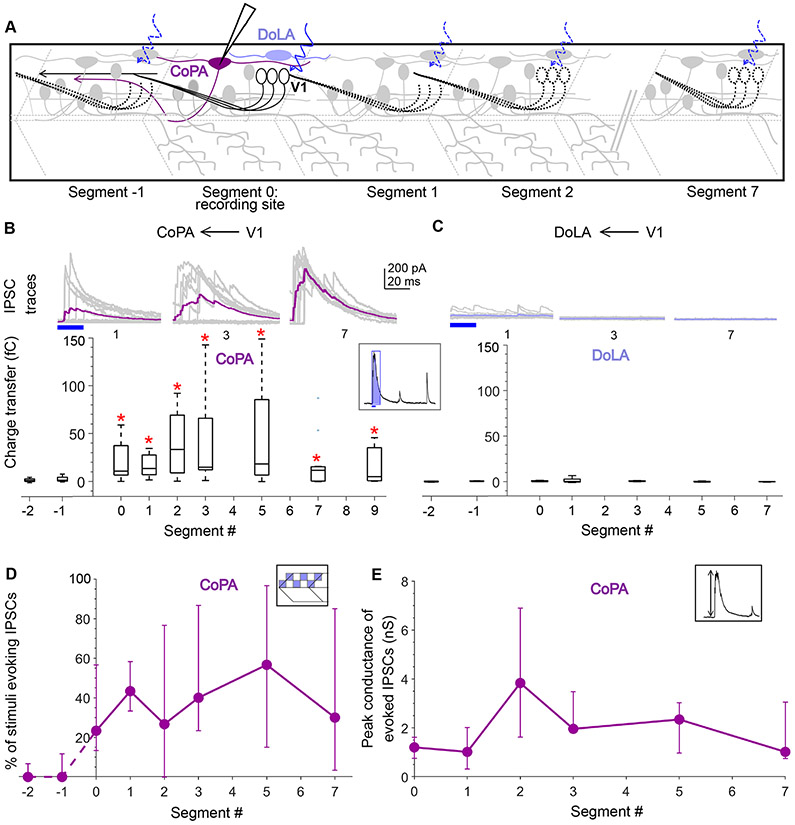
Figure 5: Dorsal horn CoPA neurons receive both local and long-range inputs from V1 neurons.
A. Schematic of the experimental design showing intracellular recordings from CoPA (magenta) and DoLA (violet) neurons paired with optical stimulation of V1 neurons (black) along the rostro-caudal axis. B. Top: Representative overlay of 15 traces of IPSCs recorded in CoPA neurons during illumination of segments 1, 3, and 7 caudal to the recorded neuron position. Colored trace represents mean. Duration of the optical stimulus is shown as a blue bar. Bottom: Box plots showing the total charge transfer per segment recorded in CoPA neurons. Red asterisks mark segments that were significantly different from noise (p < 0.01). N = 7 to 12 neurons for each data point. C. Same as in B for DoLA neurons. N = 4-5 neurons for each point. D, E. Comparison of the number of squares in the optical stimuli grid that evoked IPSCs (D) and the peak conductance of IPSCs (E) in CoPA neurons. N = 7-12 neurons. See also Figure S5.