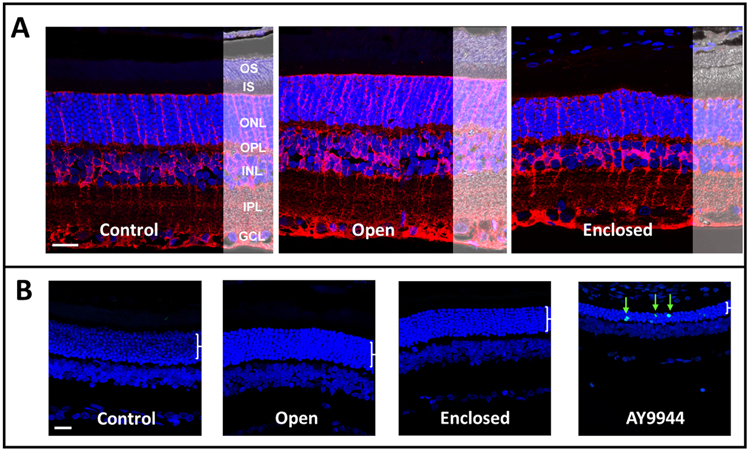
Figure 8. No obvious changes in retinal morphology or retinal cell death were observed in either blast-exposed group.
(A) Laser confocal immunofluorescence microscopy images of rat retinas (immersion PFA-fixed, paraffin embedded whole eyes) probed with antibody to glutamine synthetase (red) to label Muller glia processes, counterstained with DAPI (nuclei, blue), with Normarski image overlay to show retinal morphology. Control (non-blast exposed eyes) versus eyes from blast-exposed rats in open holder vs. enclosed holder, at 6-8 months post-blast exposure. No obvious differences in retinal morphology (e.g., signs of degeneration) were observed as a function of blast exposure, relative to control. (B) Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL, green arrows) from each experimental group and eyes harvested from AY9944-treated rats serving as a biological positive control for apoptotic cell death. No overt signs of apoptosis in the ONL or other retinal layers at 6-8 months post-blast exposure. Abbreviations: OS, outer segment layer; IS, inner segment layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Scale bar (all panels), 20 μM.