Figure 2. Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) agonists in non-alcoholic hepatitis.
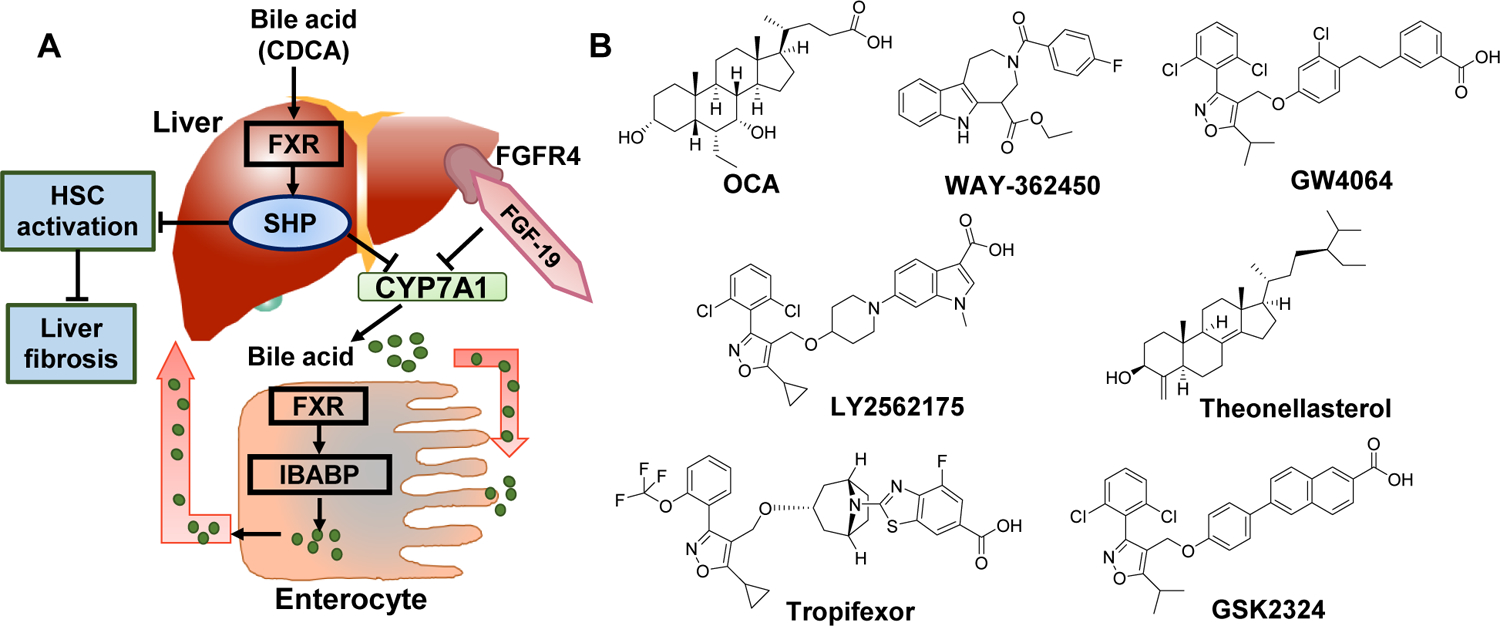
A) The role of FXRs in bile homeostasis and liver disease. B) Various FXR binding agents. CYP7A1 activity affects the overall rate of bile acid synthesis. Hepatic FXR activation reduces CYP7A1 mRNA expression by activating small heterodimer partner (SHP). FXR signaling plays an essential role in the control of hepatic de novo lipogenesis via SHP- mediated inhibition of SREBP-1c. SHP is also expressed in HSCs, and FXR ligands inhibit their activation and collagen synthesis. In enterocytes, FXR through Ileal bile acid-binding protein (IBABP), induces intestinal hormone fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19), which activates FGF receptor 4 (FGFR4) signaling in hepatocytes to inhibit CYP7A1 via triggering the extracellular stress-activated receptor kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) pathway. Obeticholic acid (OCA), a semi-synthetic bile acid analogue of 6α-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid (6-ECDCA), is used as a medication for treatment of primary biliary cholangitis. In REGENERATE trial, OCA improved fibrosis in NASH patients.
