Figure 5.
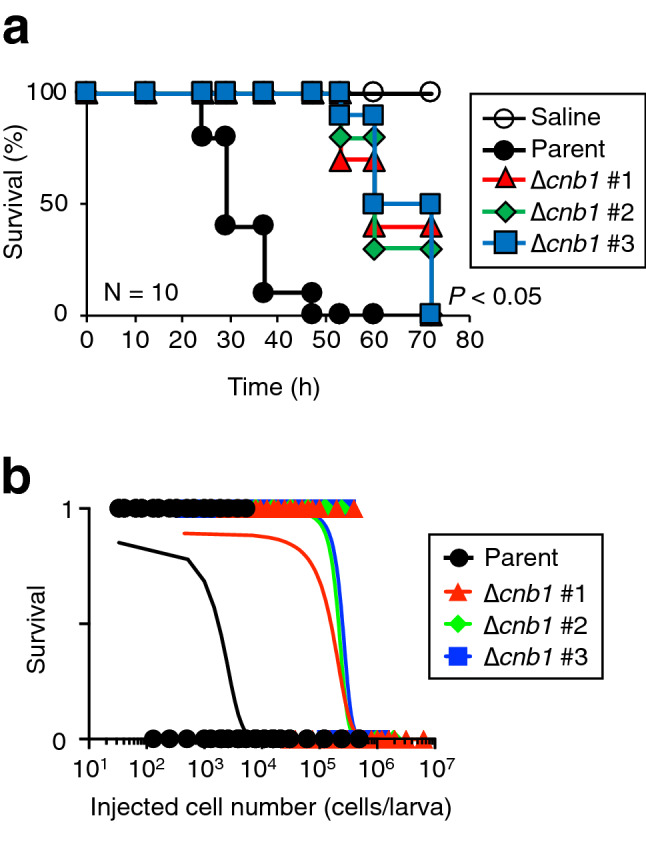
Attenuated pathogenicity of T. asahii against silkworms by cnb1 gene-deficiency. (a) Saline, T. asahii MPU129 ∆ku70 (parent strain) (5.4 × 104 cells/larva), or the cnb1 gene-deficient mutants [∆cnb1 #1 (7.1 × 104 cells/larva), #2 (5.2 × 104 cells/larva), and #3 (2.5 × 104 cells/larva)] were injected into the silkworm hemolymph and the silkworms were incubated at 37 °C. The survival of the silkworms was monitored for 72 h. The significance of differences between parent strain group and the cnb1 gene-deficient mutant groups was calculated by the log-rank test based on the curves by the Kaplan–Meier method. n = 10/group. (b) The number of surviving silkworms under a rearing condition at 37˚C was determined at 48 h after administration of the fungal cells (3.3 × 102 to 6.2 × 106 cells/larva) into the hemolymph of silkworms. Survived and dead silkworms were indicated as 1 and 0, respectively. n = 4/group. The curves were drawn from combined data of 2–3 independent experiments by simple logistic regression model.
