Fig. 1. Structure and conformational rearrangements of mGlu receptor.
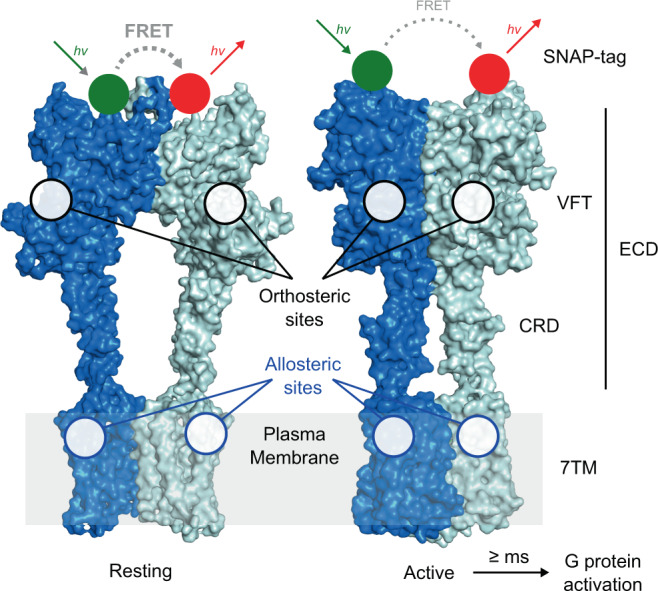
Structures of dimeric mGlu2 in resting and active conformations. The major structural elements of each subunit include the extracellular domain (ECD, comprising the Venus fly-trap domain (VFT) and the cysteine-rich domain (CRD)) and the seven-transmembrane domain (7TM). Orthosteric ligand binding sites are found in the cleft between the upper and lower lobes (black circles) of the VFT and the majority of allosteric modulators bind to sites in the 7TM (blue circles). Activation leads to a closure of the VFTs and a reorientation of the ECDs, the CRDs, and the 7TMs bringing the two subunits into closer proximity. In N-terminally SNAP-tag labeled receptor dimers this leads to a transition from a high FRET/resting to a low FRET/active state. G protein activation through interactions with the cytoplasmic side of the 7TM is reported to occur at >10 ms timescales. The shown structures were generated using PDB ID 7EPA and 7E9G.
