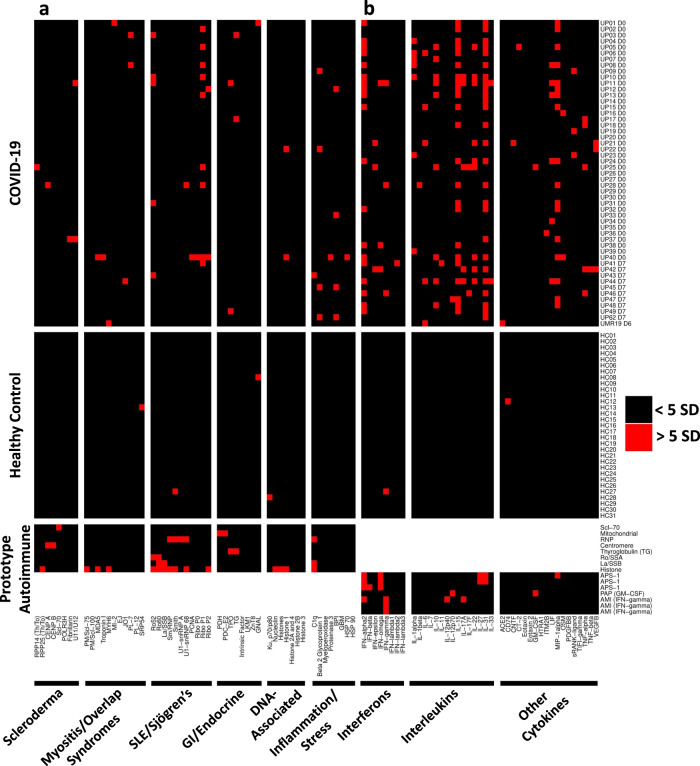
Fig. 1. High prevalence of autoantibodies in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
a Heatmap depicting serum IgG antibodies discovered using a 53-plex bead-based protein array containing the indicated autoantigens (x-axis). Autoantigens are grouped based on disease (scleroderma, myositis, and overlap syndromes such as mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), SLE/Sjögren’s, gastrointestinal and endocrine disorders), DNA-associated antigens, and antigens associated with tissue inflammation or stress responses. COVID-19 patients (top panel), HC (n = 31, middle panel), and 8 prototype autoimmune disorders (bottom panel) are shown. Colors indicate autoantibodies whose MFI measurements are >5 SD (red) or <5 SD (black) above the average MFI for HC. MFIs <3000 were excluded. b Heatmap using a 41-plex array of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and receptors. The same samples in Panel A were also analyzed for anti-cytokine antibodies (ACA). Cytokines are grouped on the x-axis by category (interferons, interleukins, and other cytokines/growth factors/receptors). Prototype samples from patients with immunodeficiency disorders include three patients with Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1 (APS-1), one patient with Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (PAP), and three patients with Atypical Mycobacterial Infections (AMI). Colors indicate autoantibodies whose MFI measurements are >5 SD (red) or <5 SD (black) above the average MFI for HC. MFIs <3000 were excluded. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.