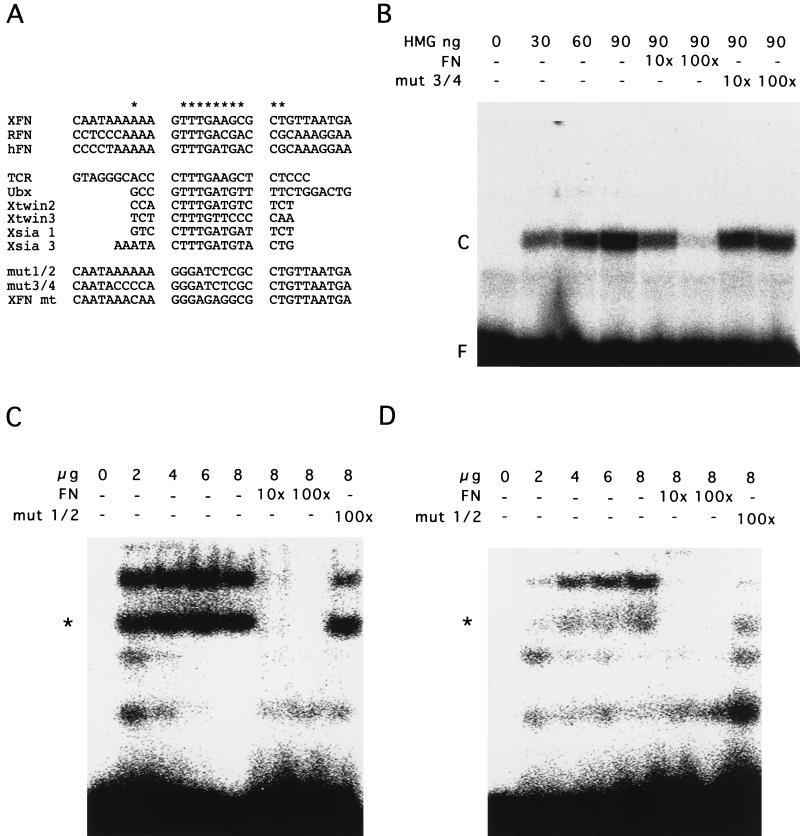
FIG. 5.
Interaction of the identified Wnt/Wg response element with HMG box fusion protein and nuclear extracts. (A) Comparison of putative Wnt/Wg response elements with the LEF-TCF consensus binding sequence in different promoters. XFN, Xenopus fibronectin gene promoter; RFN, rat fibronectin gene promoter (43); HFN, human fibronectin gene promoter (7); TCRα, T-cell receptor α (12), Ubx, ultrabithorax (46); Xtwin2 and -3, Xenopus twin (34); and Xsia 1 and 3, Xenopus siamois (3). mut 1/2 and mut 3/4, two mutated XFN sequences used for competition experiments; mt, mutated LEF-TCF target site in the −499/+20 mt construct. (B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay with the XFN oligonucleotide and a fusion protein consisting of the LEF-1 HMG box. Amounts of HMG box protein are indicated. For competition studies, oligonucleotide mut 3/4 was used. F, free oligonucleotides; C, complex of oligonucleotide and protein. (C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay with the XFN oligonucleotide and nuclear extracts of Xenopus fibroblasts (XTC). Amounts of nuclear extracts are indicated. For competition studies, oligonucleotide mut 1/2 was used. Two slower-migrating bands were identified. (D) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay with the XFN oligonucleotide and nuclear extracts of a Xenopus kidney epithelial cell line (A6). Amounts of nuclear extracts are indicated. For competition studies, oligonucleotide mut 1/2 was used. The band marked with an asterisk was specific in both XTC and A6 cells, whereas the slower-migrating band was specific only in XTC cells.