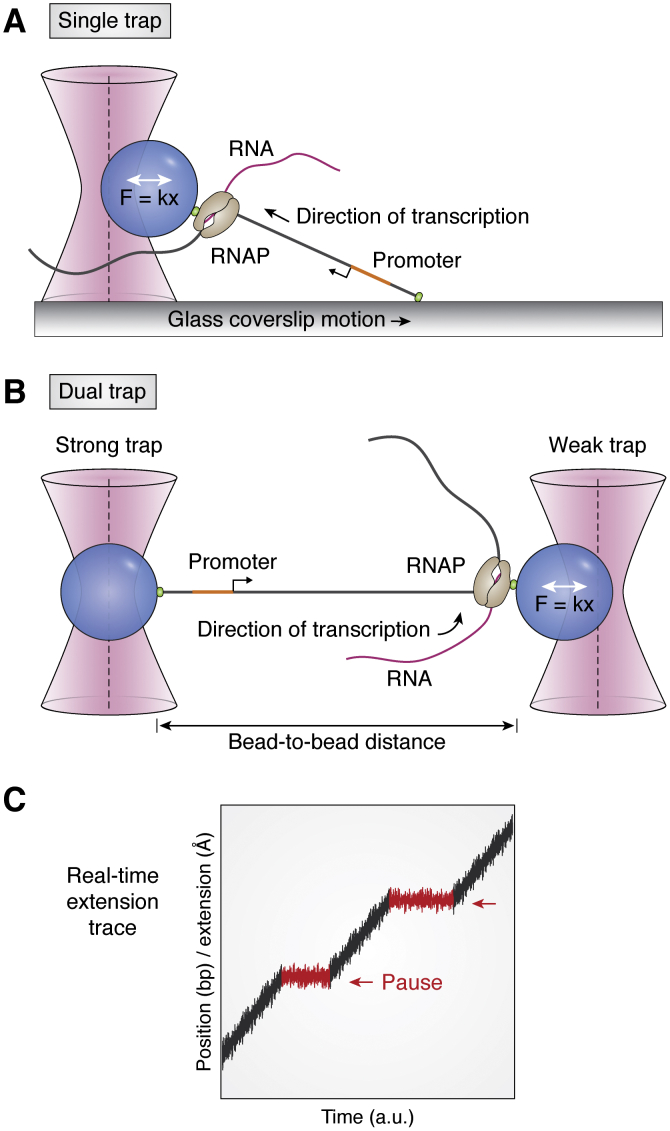
Figure 7.
RNAP translocation detected by optical tweezers.A, single optical trap system. One end of the DNA strand is immobilized on the slide surface, and the other end is dragged by the RNAP, which is tethered to the bead. B, dual optical trap system. One end of the DNA strand and RNAP are tethered to the beads. When RNAP moves to the other end of the DNA strand during elongation process, it causes the tension force change (ΔF), which can be further interpreted to the coverslip displacement (single trap) or the change of bead-to-bead distance (dual trap). C, an example of the real-time extension trace. DNA extension is plotted as a function of time. The pause events (red arrow) are observed as temporary stops with certain time intervals. RNAP, RNA polymerase.