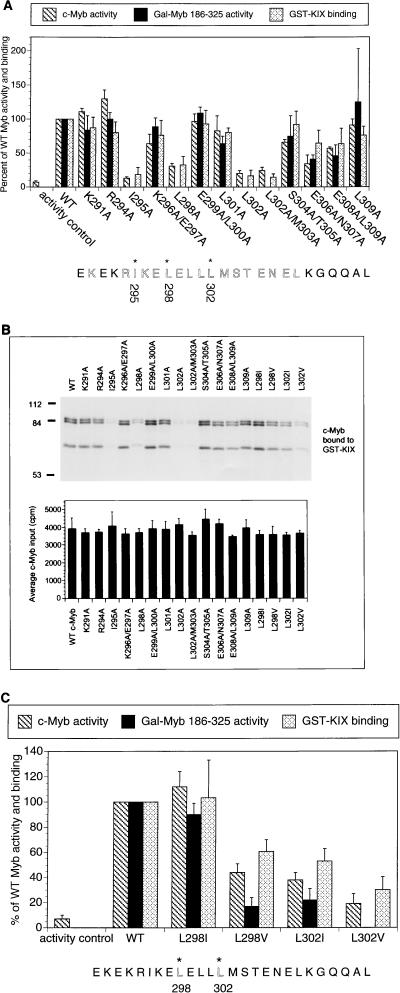
FIG. 2.
Hydrophobic residues in c-Myb are necessary for formation of a complex with KIX and for target gene activation. (A) Alanine mutagenesis reveals that Ile295, Leu298, and Leu302 are necessary for c-Myb function. Shown are activities of mutant c-Myb polypeptides, either in the context of full-length c-Myb (c-Myb activity; hatched bars) or as a Gal-Myb (aa 186 to 325) fusion protein (Gal-Myb 186-325 activity; black bars). Full-length c-Myb activity was evaluated by using a CD13/APN luciferase reporter, whereas Gal4-Myb activity was assessed with a 5×Gal4-luciferase reporter in 293 cells. The activity controls are empty expression vector control for the c-Myb transactivation assays and Gal DNA binding domain expression vector for the Gal-Myb 186-325 activity assays. Activity is compared to that of wild-type (WT) c-Myb (set at 100%). In vitro binding assays were performed by using full-length c-Myb and GST-KIX polypeptides (GST-KIX binding; stippled bars). Binding of WT c-Myb to KIX is compared to those by mutant c-Myb polypeptides. Asterisks at the bottom indicate residues in c-Myb critical for transcriptional activity and for KIX binding. Results for transcriptional activity are presented as means ± standard deviations (n ≥ 2). The GST-KIX pulldown data are presented as means ± standard deviations (n = 3). Comparable expression of mutant c-Myb polypeptides, either in the context of the full-length protein or as GAL4-Myb chimeras, was verified by Western blot assay of transfected cells (data not shown). (B) Top, representative autoradiogram obtained following SDS-PAGE of 35S-labeled c-Myb proteins bound to GST-KIX resin. Bottom, average input (40% of total, expressed as counts per minute) for each c-Myb polypeptide. Data are expressed as means ± standard deviations (n = 2). Bands of 84 and 85 kDa represent full-length c-Myb polypeptides. Although the precise amino acid endpoints were not determined, the 65-kDa band represents a C-terminally truncated c-Myb polypeptide extending through the first 600 amino acids of c-Myb and containing the KIX binding domain (aa 295 to 315). (C) Leu302 in c-Myb forms specialized contacts with the KIX domain of CBP. The effects of conservative substitutions at Leu298 and Leu302 in c-Myb on target gene activation and complex formation with KIX are shown. Activities are shown as percentages of that for WT c-Myb (hatched bars) or Gal4 Myb 186-325 (black bars) polypeptides. Results from pulldown assays (see Fig. 2B) with GST-KIX resin are also shown (stippled bars).