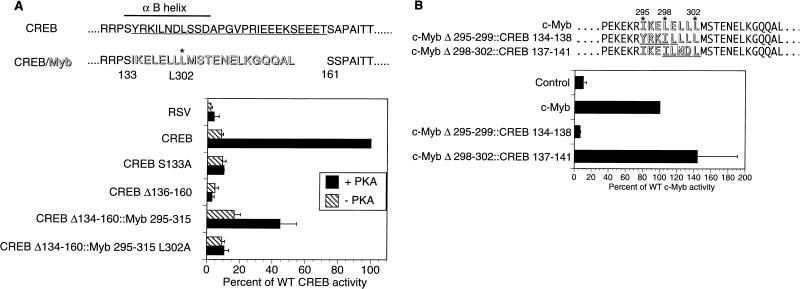
FIG. 5.
A putative α-helix in c-Myb is functionally similar to the αB region of CREB. (A) Insertion of a c-Myb fragment containing a putative α-helix rescues PKA inducibility from an inactive CREB polypeptide lacking the αB helix. F9 cells were transfected with CRE-CAT reporter and expression vectors for either CREB, CREB S133A (nonphosphorylatable), CREB Δ136-160 (lacking the αB helix), CREB Δ134-160::Myb 295-315, or CREB Δ134-160::Myb 295-315 L302A (containing the Leu302-to-Ala mutation in the Myb insert). Cotransfection with wild-type (WT) PKA (+ PKA) or catalytically inactive PKA (− PKA) expression vector is indicated. Activities are reported as means ± standard deviations (n ≥ 3) compared to that of WT CREB with PKA (100%). RSV is an empty expression vector control. CREB residues that form the αB helix are indicated by a thick line; residues deleted in the CREBΔ136-160 mutant are indicated by the thin underline; c-Myb residues (295 through 315) that were inserted into CREBΔ134-160 are shown in shadowed type (CREB/Myb). The positions of CREB aa S133 and S161 and c-Myb aa L302 are shown. (B) A portion of the CREB αB helix can substitute for the comparable region of the putative α-helix of c-Myb. Activity was tested on the c-Myb-responsive CD13/APN Luc reporter in 293 cells, along with cytomegalovirus expression vectors for either c-Myb, c-MybΔ295-299::CREB134-138, c-MybΔ298-302::CREB137-141, or an empty vector (Control). c-Myb (outlined type) sequences replaced by CREB residues (underlined and outlined type) are indicated. Activities are reported relative to WT c-Myb (100%) and expressed as means ± standard deviations (n ≥ 2).