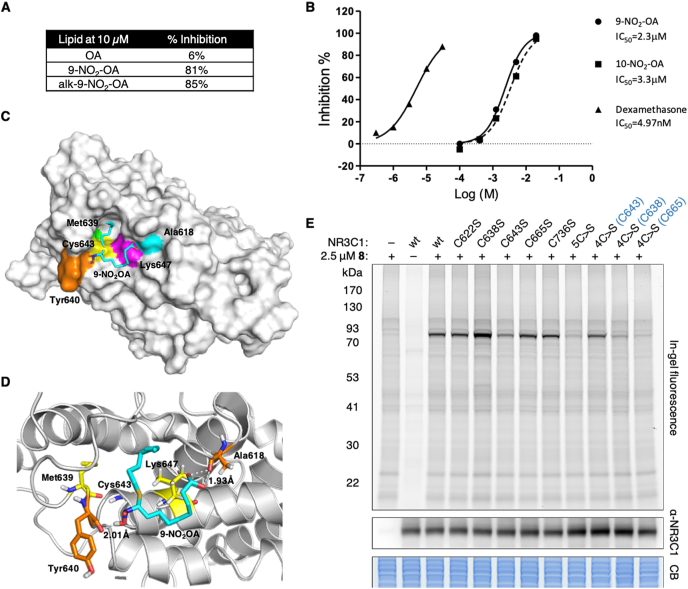
Fig. 5.
Nitro-alkylation of glucocorticoid receptor NR3C1. (A) Percent inhibition of [3H]dexamethasone binding to human NR3C1-LBD by different compounds. Compounds were screened at 10 μM in duplicates and the description of significant response (≥50% maximum inhibition) is an arbitrary criterion used in primary high-throughput screening assays. (B) Dose response curves of 9-NO2-OA and 10-NO2-OA were conducted in duplicates. The compound concentration that caused 50% inhibition of [3H]dexamethasone binding to human NR3C1-LBD (IC50 values) were determined from these curves. Dexamethasone was included as a control. (C) The most stable complex obtained for 9-NO2-OA in the NR3C1-LBD (1NHZ). 9-NO2-OA and relevant residues are colored. (D) Binding site analysis for 9-NO2-OA (Cyan) with NR3C1-LBD. 9-NO2-OA forms a covalent bond with Cys643, and hydrogen bonds with Tyr640 and Ala618 (orange residues). Hydrophobic effect was contributed by Leu647 and Met639 (yellow residues). (E) Labeling of wildtype (wt) NR3C1 and indicated mutants in HEK293T cells at 2.5 μM alk-9-NO2-OA for 1 h (2 independent biological repeats). 5C>S refers to the mutant with all 5 cysteines (C622, C638, C643, C665, C736) in the LBD mutated to serine. 4C>S(Cxxx) refers to mutants with 4 of the 5 cysteines in the LBD mutated to serine, but with the indicated cysteine remaining intact. Anti-NR3C1 and Coomassie blue (CB) stain act as loading controls for the fluorescence gel. Selected protein molecular weight markers are indicated. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)