Figure 3. Interplay between Plx1 and PP2A‐B56 on Apc1‐loop500 .
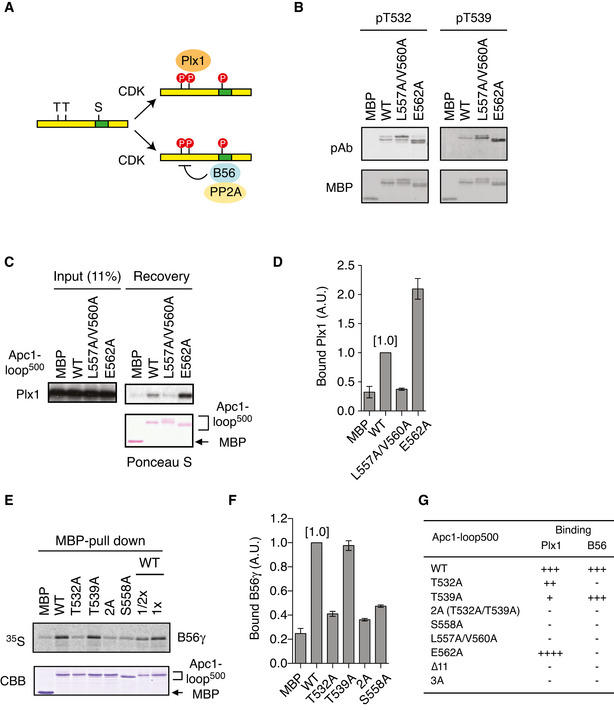
- Apc1‐loop500 is the hub for both Plx1 and PP2A‐B56 phosphatase. CDK sites (T or S) and B56‐binding site (green) on Apc1‐loop500 (yellow bar) are shown. Bindings of Plx1 and B56 to Apc1‐loop500 depend on phosphorylation of CDK sites. The PP2A‐B56 associated with Apc1‐loop500 may dephosphorylate CDK sites.
- Phosphorylation status of T532 and T539 in Apc1‐loop500 varies depending on mutations in the B56‐binding site. MBP‐fused Apc1‐loop500 WT or its derivatives (L557A/V560A and E562A) was incubated with anaphase extracts supplemented with non‐degradable cyclin B at 23°C for 1 h. The proteins were recovered by amylose beads, separated by SDS–PAGE and detected by immunoblotting with phospho‐specific (pAb) or MBP antibody.
- Plx1‐binding assay using MBP‐fused Apc1‐loop500 fragments with mutations in B56‐binding site. The Plx1 binding to Apc1‐loop500 WT or its derivatives (L557A/V560A or E562A) was analysed as described in Fig 1B.
- Quantification of (C). The bar graph is quantification of bound Plx1. The intensities of WT were arbitrarily set to 1.0. Error bars, SEM from three independent experiments.
- Binding assay using MBP‐fused Apc1‐loop500 fragments and B56γ MBP‐fused Apc1‐loop500 WT or its derivatives (T532A, T539A, T532A/T539A (2A) and S558A) was incubated with the 35S‐labelled Flag‐B56γ in anaphase extracts supplemented with non‐degradable cyclin B at 23°C for 1 h. The bound proteins were recovered by amylose beads, separated by SDS–PAGE and detected by autoradiography or Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining. The recovery of WT (×1/2 and ×1) was run as a standard.
- Quantification of (E). The bar graph is quantification of bound B56γ. The intensities of WT were arbitrarily set to 1.0. Error bars, SEM from three independent experiments.
- Summary of Plx1 and B56 binding to Apc1‐loop500 derivatives. The abilities of Apc1‐loop500 fragments carrying the indicated mutations are shown. The B56 bindings to ∆11 (deletion of 11 residues including B56‐binding site) and 3A (T532A/T539A/S558A) were tested previously (Fujimitsu & Yamano, 2020).
