Figure 6. Increased Plx1 binding to Apc1‐loop500 induces premature APC/C activation and delays dephosphorylation of APC/C during mitotic exit.
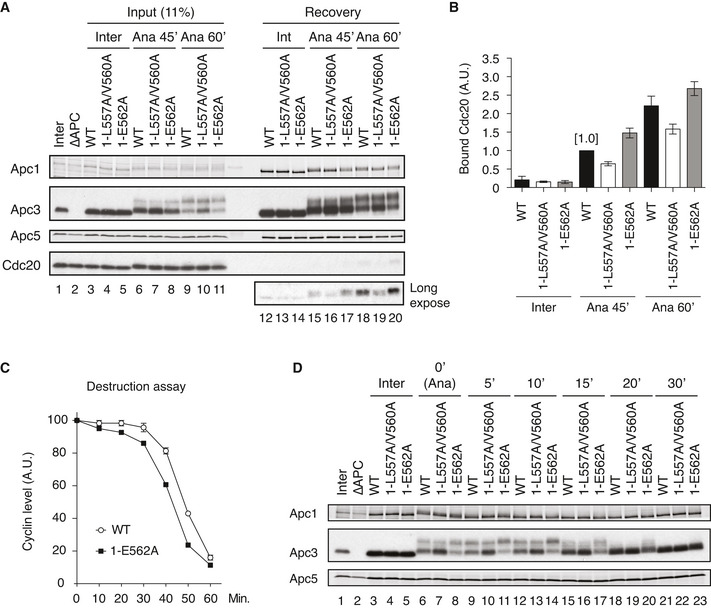
- Cdc20‐binding assay in Xenopus egg extracts. The Cdc20‐binding activities of WT APC/C and Apc‐loop500‐mutant APC/Cs with mutations (1‐L557A/V560A or 1‐E562A) were analysed as described in Fig 2A.
- Quantification of (A). The bar graph is quantification of bound Cdc20.The intensities of WT control at Ana‐45 min were arbitrarily set to 1.0. Error bars, SEM from three independent experiments.
- Premature activation of a mutant APC/C (1‐E562A) in Xenopus egg extracts. The purified recombinant WT APC/C or Apc‐loop500‐mutant APC/C (1‐E562A) was incubated with its substrates (35S‐labelled cyclin B and a version of cyclin B lacking the N‐terminal 67 residues, ∆67) in APC/C‐depleted (ΔAPC) interphase extracts supplemented with non‐degradable cyclin B at 23°C. Samples taken at indicated time points after addition of substrates were analysed by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography (Appendix Fig S7A). The relative cyclin levels are shown, normalised with reference to the intensities found at time 0 for each time point. Error bars, SEM from three independent experiments. A representative result is shown in Appendix Fig S7A.
- APC/C dephosphorylation after inactivation of CDK. The purified recombinant WT or Apc‐loop500‐mutant APC/Cs with mutations (1‐L557A/V560A or 1‐E562A) was incubated with APC/C‐depleted (ΔAPC) in anaphase extracts supplemented with non‐degradable cyclin B at 23°C for 1 h (Ana). After addition of p27 (0.3 µM), the samples taken at time points shown were analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. “Inter” denotes interphase.
