Figure EV2. Dnmt3a/b‐dependent CpG methylation and transcriptional changes during differentiation of adult hippocampal NPCs into neurons.
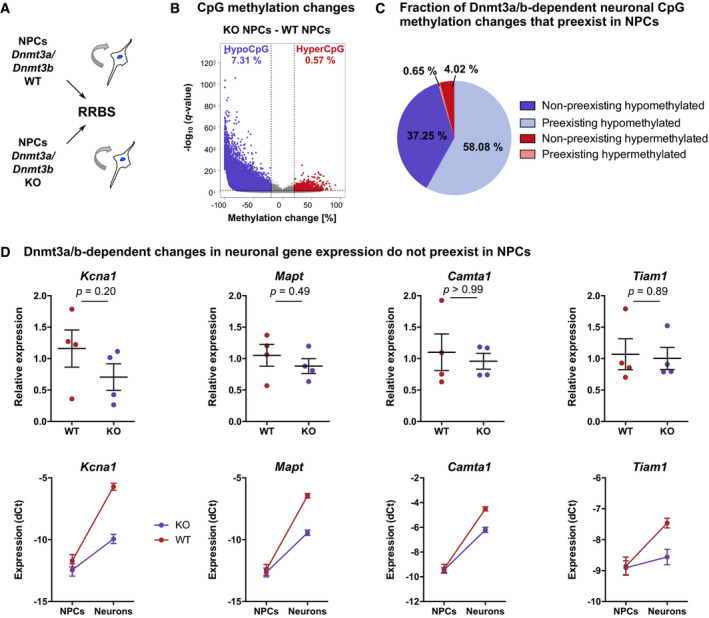
- RRBS was performed on in vitro cultures of proliferating NPCs that were derived from the hippocampus of adult Dnmt3a/b‐WT and KO mice (n = 3 cell lines per genotype).
- Significantly differentially methylated CpGs between KO and WT NPCs (q < 0.05; absolute methylation differences greater than 20%) are highlighted in violet (hypomethylated CpGs—hypoCpG) and red (hypermethylated CpGs—hyperCpG). Percentages of differentially methylated CpGs among all CpGs covered by RRBS are indicated with the respective color.
- Dnmt3a/b‐dependent methylation changes in neurons (see Fig 3B) separated into CpGs that were differentially methylated already in NPCs (preexistent) compared to CpG methylation differences that emerged during the course of neuronal differentiation (non‐preexistent). CpGs were further divided into hypomethylated or hypermethylated sites in KO versus WT neurons.
- Dnmt3a/b mediate the transcriptional up‐regulation of neuronal genes during neuronal differentiation. Depicted are expression fold changes in KO NPCs versus WT NPCs (top) and normalized expressions (normalized to Actb) in NPCs and neurons (bottom). Depicted P‐values are from Mann–Whitney test (n = 4 cell lines per genotype). Depicted are data points for every culture with genotype means ± SEM (top) or genotype means ± SEM (bottom).
