FIGURE 1.
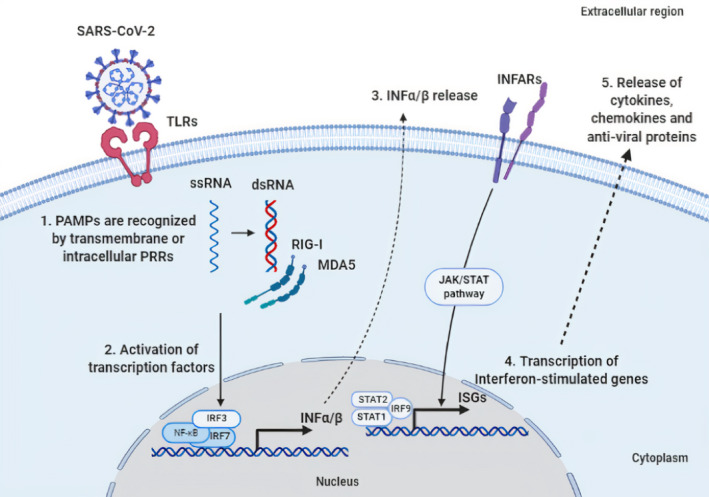
Basic molecular mechanisms of innate immune cells in response to SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. (1) Cells of the innate immune recognize pathogen‐associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), like viral proteins and double‐stranded RNA (dsRNA), through transmembrane or intracellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as toll‐Like receptors (TLRs) or RIG‐I‐like receptors (RLRs) consisting of the retinoic acid‐inducible gene‐I (RIG‐I) and the melanoma differentiation‐associated protein 5 (MDA5). (2) This recognition leads to the activation of the transcription factors, nuclear factor kappa B (NF‐κB), interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), and IRF7, resulting in the expression of interferons (IFNs) α/β. (3) The binding of INF‐α/β to interferon‐alpha/beta receptor (INFAR) activates the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, which leads to (4) the expression of interferon‐stimulated genes (ISGs), by the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), STAT2 and IRF9, and (5) finally to release of different cytokines, chemokines and anti‐viral proteins. The figure was designed by the biorender in silico tool (https://app.biorender.com/).
