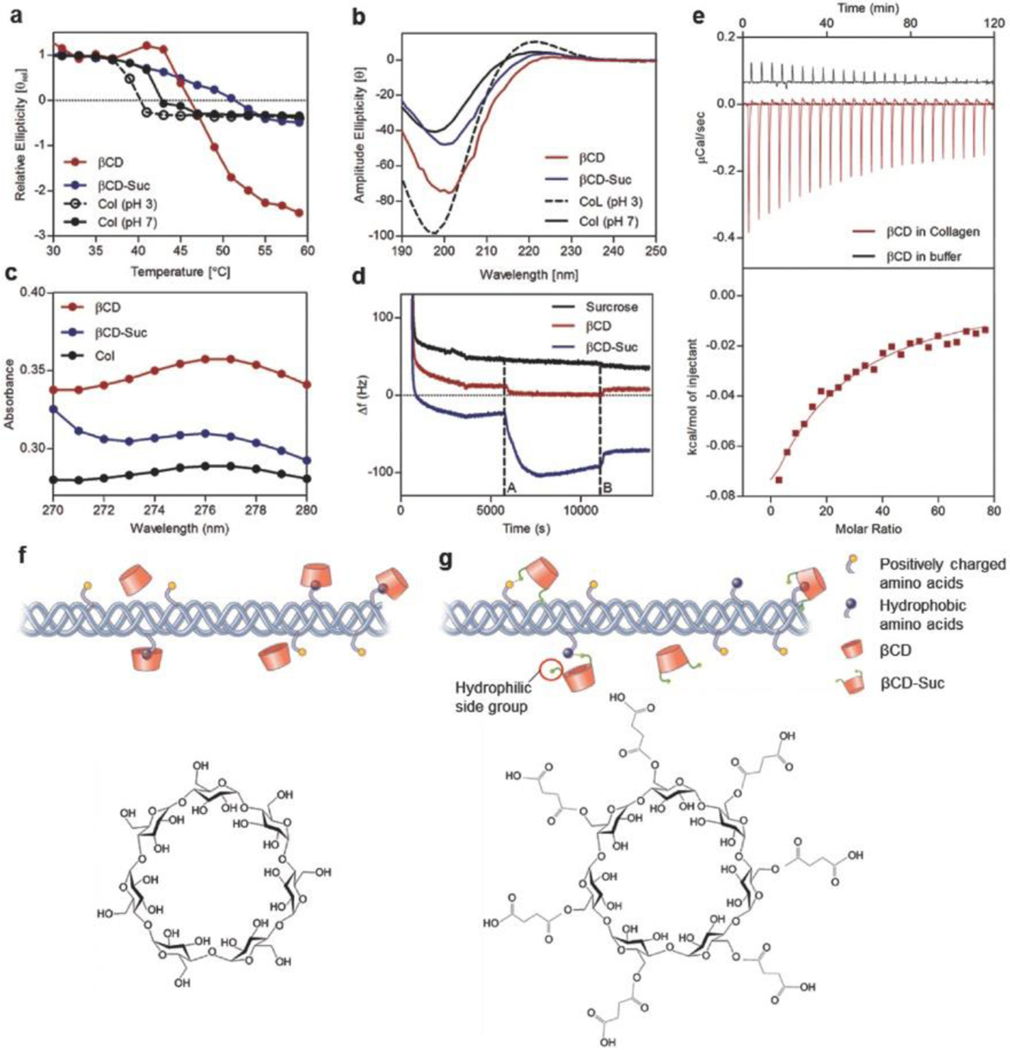
Figure 3.
Collagen–cyclodextrin molecular interactions and effect on fibril formation. a) Circular dichroism spectroscopy among groups to demonstrate changes in thermal stability following molecular interactions between soluble collagen and βCD, b) CD spectrum of collagen triple helix with and without CD at a temperature of 5 °C. c) Shift in UV–vis light spectrum absorbance peak following incorporation of βCD and βCD-Suc into soluble collagen. d) Frequency change associated with βCD and βCD-Suc deposition and binding to collagen coated substrate via QCM analyses (frequency overtone n = 5). e) Quantification of binding affinity of βCD with collagen via ITC at 20 °C. f) Schematic showing interaction of collagen hydrophobic groups with hydrophobic inner core of βCD and chemical structure. g) Incorporation of βCD-Suc in collagen involves additional interaction of the highly hydrophilic succinyl side chains and βCD-Suc chemical structure.