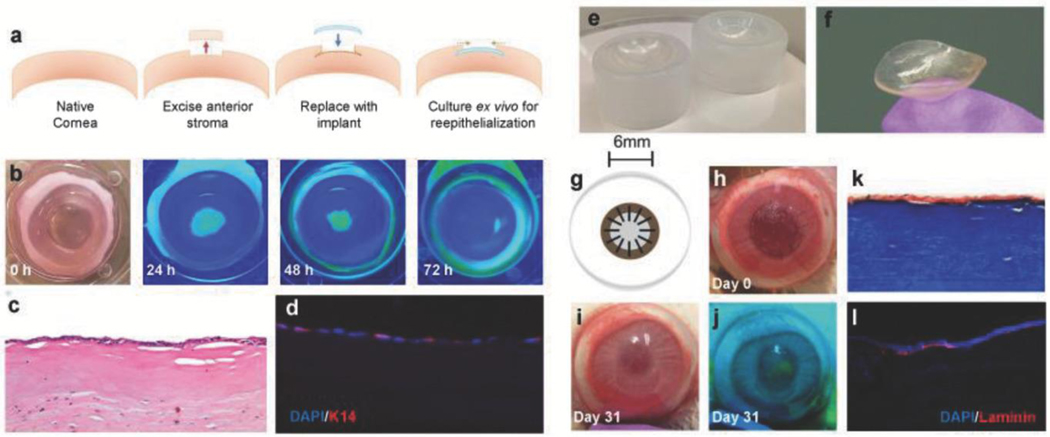
Figure 4.
Functional compatibility and surgical in vivo performance of biomimetic collagen-CD implants. a) Schematic outlining implantation of CD/ Col materials in ex vivo rabbit corneas. b) Progress of corneal epithelial wound healing over 72 h observed via fluorescein staining. Yellow-green staining under blue light indicates regions without epithelial cell coverage. c) Proliferation of epithelium observed across implants at 72 h using H&E histology. d) DAPI (blue) and K-14 (red) staining via immunohistochemistry of implanted ex vivo cornea sections to visualize cell maturation and functional epithelium. e) Custom molds used for manufacturing implants with desired curvature. f) Lenticularly shaped βCD/Col corneal implants with curvature of healthy cornea. g) Schematic of in vivo implantation of corneal implant and affixation using interrupted sutures. h) Gross image of the in vivo ocular surgery in the rabbit model on the day of surgery. i) Gross image of the in vivo ocular surface at 31 d. j) Fluorescein staining (under blue light) at day 31 to monitor progress of reepithelialization over βCD/Col implant. k) Histological analysis of sections stained using Masson’s Trichrome to visualize implant after 14 d. l) Immunostaining for laminin (red) and DAPI (blue) in peripheral and central wound regions. Laminin proteins are expressed by epithelial cells after maturation.