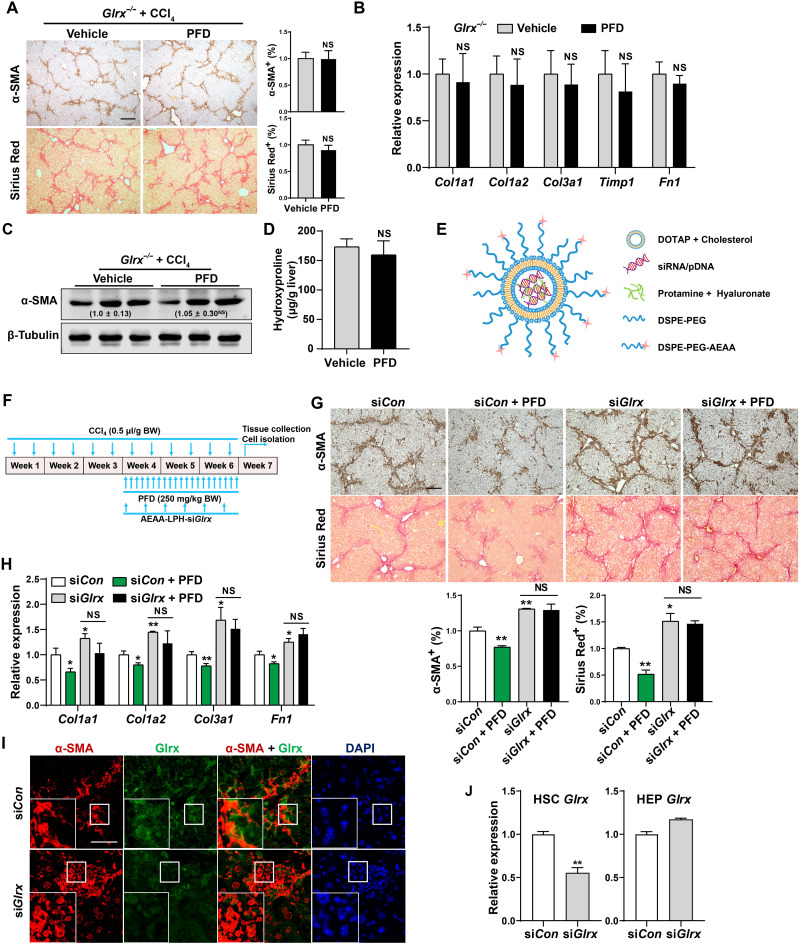
Fig. 3. Glrx depletion in HSCs abolishes the anti-fibrotic activity of PFD.
(A to D) Eight-week-old male Glrx−/− mice were subjected to the CCl4 model and treated with vehicle or PFD (250 mg/kg body weight) by gavage daily for 8 weeks (n = 6). α-SMA immunostaining and Sirius Red staining with quantifications on the right are shown. Scale bar, 200 μm. (A) mRNA expression of fibrogenic genes (B), protein expression of α-SMA with the relative quantification values labeled (C), and measurement of the liver content of hydroxyproline (D). (E) Schematic representation of the AEAA-conjugated nanoparticles for the delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) or plasmids. (F to I) CCl4-treated mice were subjected to nanoparticle regimen and PFD treatment by daily gavages as outlined in (F). α-SMA immunostaining and Sirius Red staining with quantifications at the bottom (n = 4) (scale bar, 200 μm) (G), hepatic mRNA expression of fibrogenic genes (n = 3) (H), and immunofluorescence staining of α-SMA and Glrx in fibrotic livers are shown. Magnified areas of corresponding smaller boxes are shown in the larger boxes. Scale bar, 100 μm (I). (J) Glrx mRNA expression in HSCs and HEPs isolated from mice subjected to a single injection of AEAA-conjugated nanoparticle siCon or siGlrx after a 3-week CCl4 treatment (n = 3). Data are means ± SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. Data in (A), (B), and (D) were analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t test. Data in (G), (H), and (J) were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance with the Tukey’s post hoc test.